The roof is not only protection from various atmospheric phenomena, but also the aesthetic beauty of the whole building. The unique design and structure will give individuality to any home.
Today there are a huge number of various types of roofs. All of them are used in construction, both private houses and multi-storey buildings. Regardless of the type, all the roofs consist of two main parts. The supporting structure is represented in the form of rafters and crates and the roof itself.
The shape of the roof is chosen depending on various factors. These include: the size of the building and the purpose of the building.
Roof types
Now the most common are the following types of roofs:
- single slope;
- gable;
- chetyrehskatnaya;
- flat;
- hip.
All other varieties are derived from these types.
Shed roof
Shed roof is the easiest option roofing. The name speaks for itself. This roof has only one ramp. Such structures are mainly used for small private houses, cottages, as well as in the construction of the garage. Such roofs have several advantages. The first distinct advantage is the ease of installation. Indeed, the construction of a shed roof does not require the involvement of many people and special equipment. The second advantage is the use of a minimum amount of building material. That is why the shed roofs are widely used in the construction of garages and country houses.
The angle of inclination of a single shed roof is often less than 25 degrees, so the wind does not greatly affect the integrity of the structure.
There are, of course, disadvantages that should be considered when using a shed roof. The main disadvantage is the absence of an attic. Another disadvantage is the inconspicuousness of a shed roof. It does not look as impressive as, say, a gable or chetyrehskatnaya.
Gable roof
The gable roof is a roof that has two ramp sloped to the outer walls. This type of roof is considered optimal for the construction of small houses. In this embodiment, the rafters abut each other. They make up pairs that are tied together by a crate. At the ends, this roof has triangular walls. Under the roof is set loft. This advantage allows gable roofs to remain the most popular option in modern construction. In addition, the appearance of a gable roof is much more attractive than that of a single slope.
If we talk about the installation process, it is quite simple. All rafters are installed in pairs parallel to each other. They communicate with each other by crates. The lathing is made of the simplest bars. Then various insulating materials are laid, and only after that the roof itself is mounted.
Quadrant roof

The four-slope roof is one of the most common options today. It has an attractive look and high durability. The four-pitch roof can be either hip or hip. Tent option consists of four triangles that converge into one, forming a peak.
This option is used in cases where the building box is a square. If the box of the building is rectangular, then in this case a hipped four-slope roof is installed. it consists of two triangles and two trapeziums. Of course, this design is more complicated, but it looks more attractive than the roof tent version.
The height of such a roof may be different. It is pre-calculated before installation. The four-pitched roofs are now very popular, however there are certain drawbacks to them. The most important is the complexity of the design. Such roofs, especially the hip version, require the attraction of additional labor, and the construction is sufficiently complex.
Therefore, if we are talking about a simple small building or a summer house, then it is worth trying to install another simpler option in order not to get a pretty penny.
Hipped roof
Hip roof is now widespread throughout construction. She has an attractive design as well as beauty. Many install a similar roof on their private houses or cottages.
Hip roof forms a pyramid. At its base should always be square. Its constructive elements are four triangles whose vertices converge at one point.
This type of roof saves on construction material, as it does not provide for the installation of gables. Naturally, the base must necessarily have a square, otherwise the construction will not turn out to be complete. It is necessary to strive for a square base, but you can do something similar to this geometric shape. Most importantly, all the vertices of the triangles meet at one point.
There is one very significant drawback with hipped roofs - this is the complexity of the roof system.
Flat roof
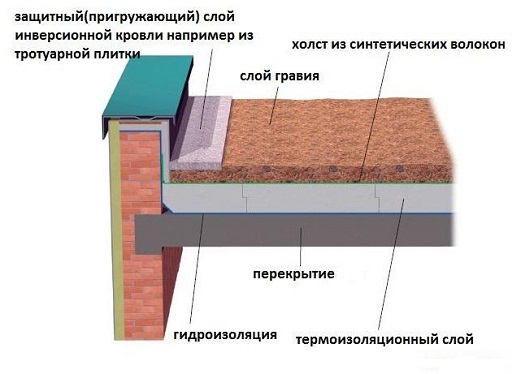
Flat roofs are used in the construction of high-rise public and residential buildings. Such roofs are very often called bescherdnymi. It is considered that such roofs are more economical than pitched ones.
For the installation of a flat roof, it is necessary to expend significantly less material than for the installation of a sloping roof of any option. The surface area is significantly less than the area covered by the pitched variants That is why flat roofs are used in high-rise construction. The material that is put on such a roof can be any, even the cheapest. Common slate is most commonly used. Such roofs are not visible from the ground. The beauty of such structures is in second place. On the first - construction savings.
There are several types of flat roofs: traditional, inversion, operated, green and so on. All these types are widely used in high-rise construction.
Roof structure
Any roof consists of three components: the carrier, thermal insulation and the roof itself.
Let us consider in more detail each component.
The most commonly used tree in the form of rafters. They can be sloped or hanging. Suspended rafters lean ends and the middle part of the walls of the building. The hanging ends rest on the walls of the building without the use of intermediate supports.
All rafters are mounted vertically. In this case, the minimum distance between them must be at least one meter. All rafters communicate with each other by crates.
Elements of truss construction are made of bars.
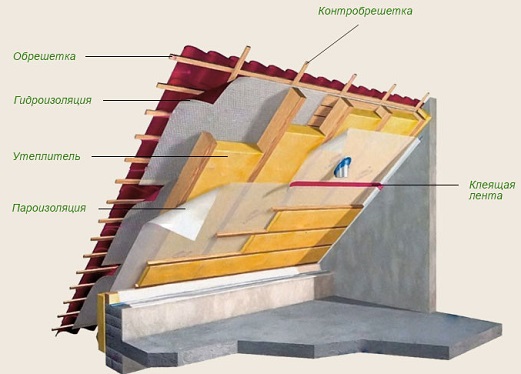
Thermal insulation layer of the roof
If we are talking about non-residential attic room, the attic flooring is subjected to insulation. In the case when it comes to the attic, it requires insulation of all surfaces.
For insulation used a variety of materials. You can use the usual mineral wool, but it will have to lay additional layers of vapor barrier and waterproofing. Thermal insulation is needed for any residential building. If we are talking about a summer cottage, you can do without it.
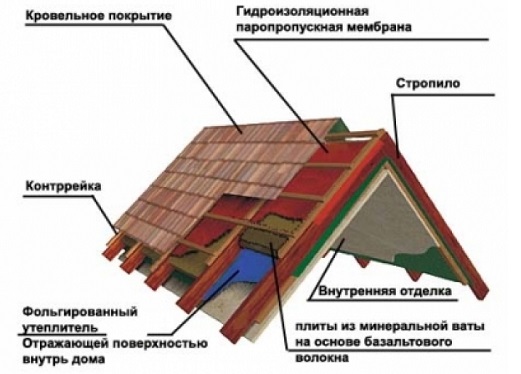
Roofing roof
The roof is the topmost layer of the roof. Roof coverings currently exist a huge amount. The most widespread slate and metal. Their main goal is to protect the building from the harmful effects of the external environment.
Roof angle
The angle of the roof depends on many different factors. The main ones are: the material from which the roof is made, the type of roof, the climatic features of the region in which the construction is made.
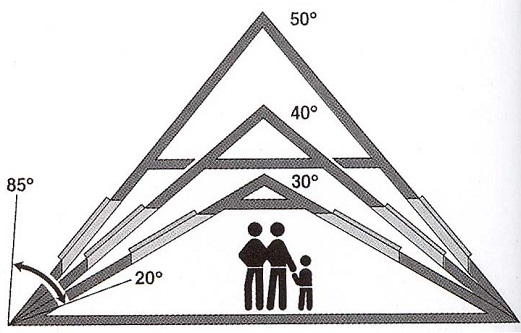
All these factors are necessarily taken into account when calculating the angle of inclination. With a large amount of precipitation, the angle increases, and with strong winds decreases. The most effective angles are from 10 to 60 degrees.
The height of the ridge of the roof and raising the rafters are determined with the help of a square. You can also calculate these values. To do this, the span width is divided in half, and then multiplied by a certain coefficient from the table.
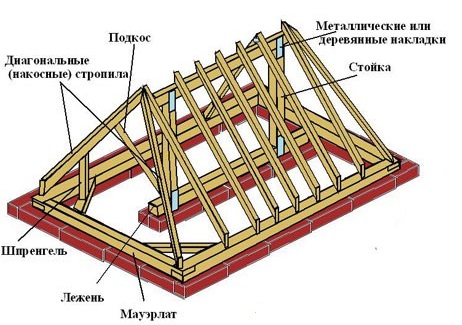
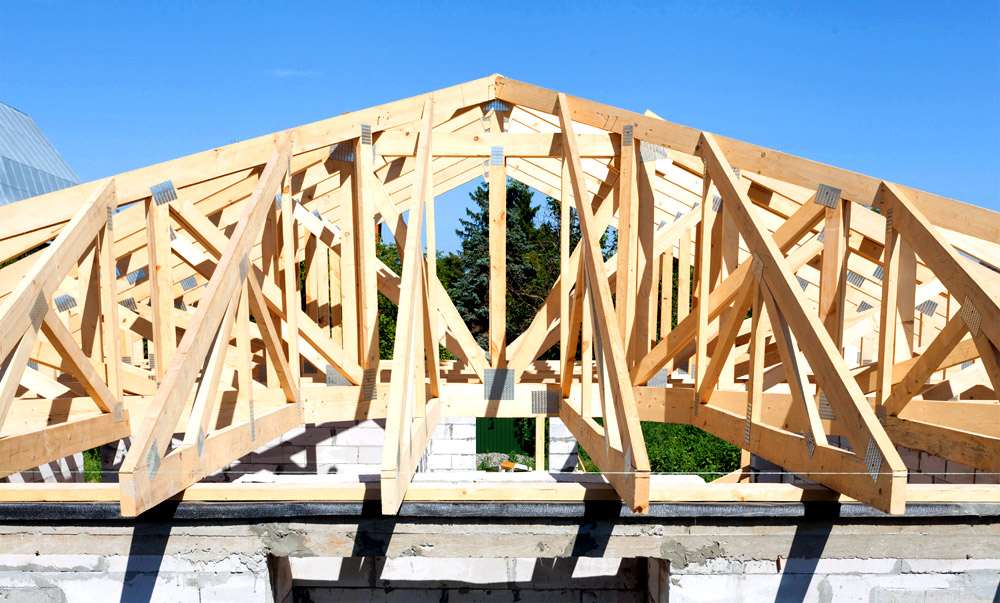
Roof rafter system
Rafters and roof trusses are of two main types - naslonny and hanging. The main truss at the moment - a triangle. It is the most rigid and economical. If we talk about roof trusses, then they consist of complex roof beams, racks, struts, and so on.

Suspended rafters. Such structures are installed in houses with an average load-bearing wall. Consist of two inclined truss legs. Their lower ends rest on the longitudinal bars, and the upper ones on the ridge girder.
Hanging rafters. They are used where there are no internal supports. They rely solely on exterior walls. They consist of sloping truss legs and a horizontal bar for the perception of thrust from truss legs.
How to build a roof properly do it yourself
Consider the option of installing a pitched roof with your own hands, as the most common today. Consists of the following sequence of actions:
- installation of rafters;
- installation of ridge beam;
- the device obreshetki;
- roofing.
Consider the process of installing the roof do it yourself. Sometimes the rafters are lowered over the edge of the wall. This is done to ensure that moisture that drains from the roof does not fall on the walls of the house.
The rafters themselves gather on the roof. Moreover, all elements must be prepared in advance. Upstairs only assembly. The result is a truss farm, which consists of two truss legs, puffs and racks. After assembly, the structure is raised vertically to the very place where it should be installed. Next, it is attached to the power plate. As additional temporary fixings boards are used.
After that, all trusses are connected by a ridge bar. After that, you can begin mounting crates. The material can be used unedged board with a thickness of 25 millimeters. It significantly reduce the cost of the roof. Each board is nailed to the rafters with nails, the length of which is 70 millimeters.
The design of the batten depends largely on what material will be laid on the roof. If you plan to use metal tile, then unedged board will not be suitable for creating crates. In this case, it is better to take the timber.
Once the crate is installed, you can proceed to the installation of roofing. It is very important to check the flatness of the battens and trusses before starting work.
Roof mounting

Installation of the roof - this is quite complicated. In most cases, you will have to seek outside help. Alone, the roof is quite difficult to mount.
Installation of the roof consists of several stages. It will be a question of a house where people live all year round, that is, it is necessary to install not only the crate, but also thermal insulation.
The entire installation process will include the following steps:
- installation of truss system;
- installation of the batten;
- laying insulation;
- installation of roofing material.
As you can see, the work is quite voluminous, but interesting. Its implementation must be approached very carefully.
So, it all starts with the installation of a truss system. It is set in place. Pre-prepared bars for rafters on the ground.
Once the rafters are installed, you can proceed to the installation of crates. It can be made from both boards and bars. It largely depends on the type of building and the type of roofing material.
Thermal insulation is necessary in those houses where year-round living is planned. In addition to the thermal insulation material, it will be necessary to install waterproofing and vapor barrier to protect the house from external weather factors.
The last stage is the installation of roofing. Currently, the most popular is metal. It is worth remembering that if you use this material, you will have to make the crate of wooden bars, as the boards do not fit.
Roof - it is a constructive element, protecting the building from above from external influences of nature. The main types of roofs are: dacha, bescherdachnye, operated roofs, long-span flat and spatial coverings.
The main purpose of the roofs - protection of the building from weathering. The enclosing structure consists of the upper waterproof layer of the roof, wooden flooring - sheathing, roof trusses that transfer the load from the own weight of the roof, snow, wind to the walls and internal supports. The outline of the roof is determined by the contour of the building, as well as architectural considerations and the properties of the roofing materials used. Depending on the number of slopes and geometric shape, the main types of roofs are:
- Single Shed
- Gable with forceps or gables.
- Chetyrehskatnye (poluvalmovye).
- Tent Roofs.
Single pitch roof the simplest version of the enclosing structure, since its design is simple to manufacture and does not require large expenditures on materials. Such roofs have a low angle, less windage. This roof is designed for buildings where there is usually no organized drain. Most of these structures are outbuildings, where the slope of the roof slopes is provided by different height of the walls.
Depending on the materials of the roof depends on the angle of the roof:
- For rolled materials the slope may be 5-7 degrees
- For metal and other sheet coatings of at least 30 degrees in warm climates, 45 is a humid climate.
Gable with forceps or gables
Dvukhskatna or gable roof consists of two slopes, directed in opposite directions, which converge at the same upper point (ridge girder), and the triangular end walls formed in the planes of the slopes are called tongs or gables. The rafter construction of the dual slope roof, depending on the shape and span, may be either nylon or trailing.
Rafter system of the sloped roof slope type.
This type of roof is used in buildings with internal load-bearing walls that serve as supports for the structure. This variant of the roof construction is used mainly for small spans of the building up to 7 m, if the distance is more than 7 m, additional pillars are required to be installed in order for the system to comply with its rigidity and be geometrically unchanged. This type of roof is a complex process of installation and work of the responsible team of roofers who will perform a range of works in accordance with regulatory documents.
- Fencing of bearing walls from moisture
- Very aesthetic appearance due to the hanging of the roof slopes behind the walls.
Rafter roof system of trailing type.
Suspended rafters are systems in which the upper ends of the rafter legs rest against each other and are supported by weight, and the lower ends are supported by fixed supports (floor beams or power plates). In this case, the main difference lies in the fact that the suspended rafters do not cause the structure to collapse from temporary loads and its own weight, while the hanging systems give thrust, perceived by tightening. Most of the truss systems, which belong to the hanging, are the rafters combined, because they use the following supporting elements: struts, headstock, pillars, ties.
The main advantages of such roofs are:
- Simplicity in the manufacture of construction.
- The greatest margin of safety of the system.
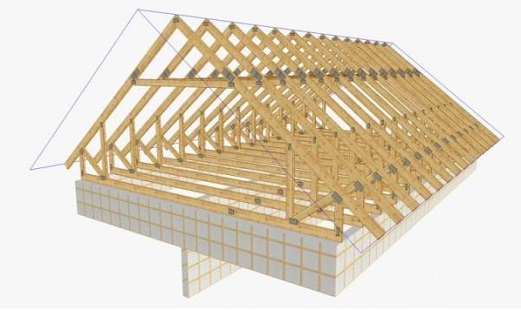
Four-Rolled
Quadrant roof has ramps on four sides. It is also called tent or hip, and the slopes from the end walls - hips. Such roofs, as a rule, do not require the construction of gable walls, but the construction of their rafters is more complex. The hip construction as a whole consists of the same elements as a simple dual-pitch roof, but its design features require additional framework components. Another type of hip system is half-hinged (if the ramps cut off the floor of the gable, that is, they have the shortest length along the slope line than the main ramps). The half hip may be located at the top in the form of a triangle, forming a trapezoidal gable.
The elements of the chetyrehskatnoy roof include:
- Mauerlat - a timber laid on the upper part of the external walls and receiving the main load from the roof;
- Lezhny - the internal basic bars laid on bearing walls or columns;
- Rafters - side and diagonal, or nakosny. The side rafters form a trapezoidal slope of the roof, the side rafter - hip.
- Racks and Sprengel - vertical supports supporting the truss system;
- Ridge cant or girder - horizontal support for rafters in the upper part of the roof. It is placed on the rack and secure. Hip roof is performed without a ridge beam;
- Tightening or bolts - horizontal elements connecting the side rafters and not allowing them to disperse to the side;
- Narozhniks - elements laid on diagonal rafters and forming a stingray frame;
- The struts and wind beams - struts that increase the strength of the roof and its ability to withstand loads;
- Fillers - boards, forming the necessary overhang of the roof and fixed to the rafters in their lower part.
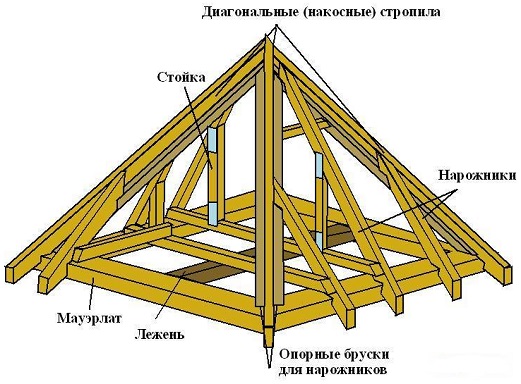
Tent roofs.
Hip roof design is a four or multi-faceted pyramid. Its slopes have the form of an isosceles triangle. Their tops converge in the center of the roof at its upper point. It should be noted that the hip roof looks more aesthetic on square bases. A certain slope of the slopes makes it possible to discharge thawed and rainwater qualitatively and reliably. The main components of the truss system at the hip roof are:
- slant (diagonal) rafters located at the corners of the base frame of the roof;
- mauerlat - beam, which is a support for the lower ends of the rafters;
- women swarms (shortened rafters), which are attached to the rafter rafters;
- footrests, which are a leg support;
- bolts, girders, logs, various additional supports to stiffen the hip roof structure.
Basic requirements (SNiP II-26-76) imposed on roofs.
The roof structure should have a degree of durability, consistent with the norms and class of the building, also provide:
- The perception of constant load (from own weight).
- Perception of temporary loads (from snow, wind and coatings arising during exploitation).
- Water resistant (no moisture transmission).
- Moisture resistant (prevent moisture from passing for a long time).
- Resistance to aggressive substances contained in ambient air and precipitation.
- Protection from solar radiation and frost.
- Do not warp, crack or melt.
The shape of the roof is divided into pitched and flat. The shape of the roof is determined by the architecture of the building and its configuration in the plan.
By roof design distinguish attic and bescherdachnye.
Depending on the temperature and humidity conditions of the upper building envelope, bescherdny (combined) roofs are divided into non-ventilated and ventilated.
By purpose, they distinguish between exploited (solariums, sports grounds, cafes, etc.) and unexposed roofs.
Pitched roofs are attic and bescherdachnye.
Attic roofs perform with a cold or warm attic. Roofless roofs can be cold (over unheated buildings) and warm (over heated buildings). Brawl roofs suit both in residential and public, and in industrial buildings for industrial and agricultural use. In industrial buildings, often on the surfaces they arrange light-aerating lanterns.
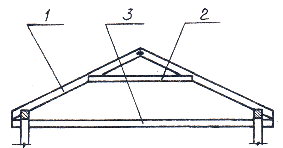
Shed roof (Fig. 1, a) slope rests on the outer walls, which are at different levels.
Fig. 1. Forms of roofs:
a - sloping, b - duo-pitch, h-tent, d-hip (chetyrehskatnaya), d-semi-hinged, e-duo-pitch with a lantern, w - vaulted, h - folded, and - domed, k - cross arch, l - gable, m - spire-like, n - spherical shell, o - from oblique surfaces, p - with internal drain, p - flat, operated
The gable roof (Fig. 1, b) consists of two planes resting on the walls located at the same level. The triangular parts of the end walls between the slopes are called tongs.
Hip roof (Fig. 1, c) has four triangular slopes, the peaks of which converge at one point.
The hip (chetyrehskatnaya) roof (Fig. 1, d) is formed from the connection of two trapezoidal rays and two triangular face skates, called hip.
The half-hinged (duo-pitch) roof (Fig. 1, e) has cut-off peaks over the end walls in the form of triangles (hips).
The gable roof of an industrial building with a longitudinal lantern (Fig. 1, e) differs from a gable roof of a residential building with a smaller inclination of the slopes and a greater width and length.
The vaulted roof (Fig. 1, g) in cross section can be outlined with an arc of a circle or other geometric curve.
The folded roof (Fig. 1, h) is formed from the connection of individual trapezoidal elements - folds.
A dome-shaped roof (Fig. 1, i) in outline represents a half of a sphere with a solid support along a ring on a cylindrical wall.
The cross vault (fig. 1, k) consists of four closed arched vaults.
A multi-tip roof (Fig. 1, L) is formed from the connection of the slopes of the planes. The ends of the walls under the gable planes are called tongs.
A spike-shaped roof (fig. 1, m) consists of several steeply dipping triangular slopes, closed to the top.
The spherical shell (Fig. 1, n) is similar in outline to a dome, but with a base supported at individual points. The space between the supports is usually arranged translucent.
The roof of oblique surfaces (Fig. 1, o) consists of several gentle planes resting on the walls.
The roof with internal drain (Fig. 1, p) is widespread in modern industrial and civil construction.
Flat to snags (Fig. 1, p) have a slope of up to 2.5%. They are satisfied in the form of sites and used for dispensaries, open-air cafes and other purposes. Although flat roofs are more expensive than pitched ones, savings in maintenance costs compensate for this disadvantage. Recently, new roof structures made of reinforced concrete precast panels have become widespread.
Roof structures. The main structural elements of the roof include load-bearing structures, vapor insulation, heat insulation and roofing.
Bearing structures perceive the load from their own weight, snow weight, wind pressure and transfer these loads to the walls or individual supports. The supporting structures are prefabricated reinforced concrete panels, complex panels of coatings of high factory readiness (with heat and waterproofing layers or only with a waterproofing layer), monolithic reinforced concrete, steel profiled flooring, wooden trusses and trusses, asbestos cement slabs.
Vapor barrier satisfied from roll bitumen, polymer film or coating materials.
Insulation is made of lightweight concrete, bitumen perlite, expanded clay, mineral wool, perlitoplastbetonnye, perlitobitumnye, perlitophosphogel gel plates, etc.
The roof is made of rolled, mastic and piece (tiles, asbestos cement plates, steel and wooden flooring) materials.
Roofs of precast concrete panels can be unexploited and exploited, bescherdny (Fig. 2, a) and attic (Fig. 2, b).
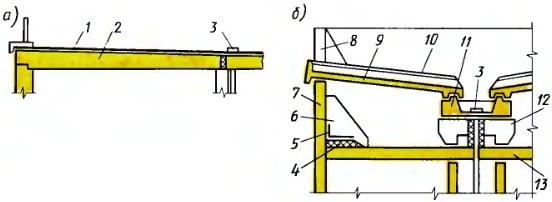
Fig. 2. Precast reinforced concrete (no) (a) and garret (b) roofs:
1 - roofing carpet, 2 - lightweight concrete panel, 3 - water intake funnel, 4 - mineral wool insert, 5 - ruberoid strip, 6 - triangular support element, 7 - frieze support panel, 8 - fencing, 9 - reinforced roofing panel, 10 - slab - flat plate, 11 - reinforced concrete catchment tray, 12 - support beam for the tray, 13 - heat-insulated floor panel of the upper floor
Precast reinforced concrete roofs suit six types:
- garret with waterproofing with mastic or painting compositions (roll-free roofing);
- garret with a roof from rolled materials;
- chaos of single-layer panels made of light or cellular concrete;
- bescherdnye of multi-layer complex panels consisting of two reinforced concrete panels, between which an effective heat-insulating material is laid;
- rackless with bearing panels of heavy concrete; on which plates from the effective warming materials are laid;
- rough construction of a multi-layer construction with backfill insulation and a coupler under the roof of roll materials.
In accordance with the Instruction for the Design of Prefabricated Reinforced Concrete Roofs of Residential and Public Buildings (VSN 35- 77), the following definitions for all roofs are made by Gosgrazhdanstroya.
The attic is a volume bounded by a covering, frieze walls and an attic floor.
The coating is an upper enclosing structure that simultaneously performs load-bearing, waterproofing, and with bescherkachnyh (combined) roofs and in warm attics, also heat-insulating functions.
Roof - the top element of the coating, made of waterproof materials and protects the building from precipitation.
The protective layer is a roofing element that protects the waterproofing carpet from mechanical damage, direct exposure to solar radiation.
An otter is a groove under a ledge formed by the laying of a clutch or a protruding edge.
Attic roofs are arranged with a cold or warm attic.
Fig. 3. Structural elements of the coating:
1 - frame bolt (beam, trusses), 2 - bearing element of the coating, 3 - vapor barrier, 4 - insulation, 5 - screed, 6 - roof, 7 - protective layer
The non-sabotage (combined) roofs perform the functions of the supporting and enclosing structures of the upper floor of buildings. The construction of a bescherdny roof consists of the following elements (fig. 3):
- bearing structure 2, which must meet the necessary conditions of strength, stiffness and crack resistance of the bone during installation and in operating conditions;
- vapor barrier layer 3, which protects against the penetration of water vapor from the premises into the thickness of the roof structure (arrange if necessary);
- heat insulation layer 4, which provides the required resistance to heat transfer;
- roofing carpet 6, which is arranged on the basis of cement or asphalt screed 5 or on the surface of the integrated panels.
Bezrulonnye roofs of residential buildings with more than five floors, satisfied with internal drainage (Fig. 4).
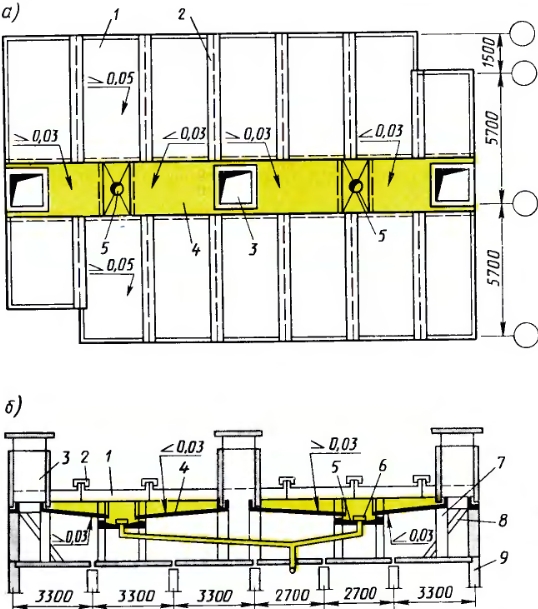
Fig. 4. The design of industrial non-roll reinforced concrete roof for large-panel residential buildings:
a - roof plan, b - longitudinal section; 1 - roofing panel, 2 - reinforced concrete lining: 3 - ventilation shaft, 4 - unified three-sided panel of the catchment tray, 5 - funnel trays, 6 - emergency overflow device, 7 - supporting element, 8 - anchor element of the frieze panel, 9 - frieze panel
A non-ventilated roofless roof consists of a series of reinforced concrete slabs 2 laid in a covering (see Fig. 3).
Ventilated bescherdnaya roof is a coating of lightweight box-like panels - asbestos cement slabs. At the same time, the supply and exhaust ducts for ventilation of the internal cavity are provided for in the design of the plates.
Complex panels of coatings of high factory readiness (Fig. 5) combine the carrier, steam and heat insulation functions. They consist of two-layer slabs, the lower layer (bearing base) of which is made of heavy reinforced concrete, the upper one - of cellular concrete or expanded clay-concrete, foam plastic, fibrolite. Complex panels can be of various designs. A pre-stressed slab is sometimes used as a bearing base.
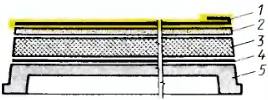
Fig. 5. The design of the integrated panel coatings increased factory readiness:
1 - roofing carpet, 2 - screed. 3 - heat insulation, 4 - vapor barrier, 5 - base plate
The vapor barrier is the roofing material of the RPP brand. The use of complex panels of coatings of high factory readiness makes it possible to exclude, in construction conditions, operations on the installation of steam and heat insulation, cement-sand screed, base primer and the implementation of waterproofing layers.
Roofs of monolithic reinforced concrete are used mainly in buildings with high seismic resistance, as well as those subject to high dynamic loads.
Roofs made of steel profiled flooring are widely used in industrial construction. The coating panel (Fig. 6, a) is made of supporting profiled decking and integrated polystyrene foam or fiberglass and mineral wool boards of increased rigidity. Galvanized steel profiles are used as supporting decking of panels (Fig. 6, b). The seams between the panels are closed using liners (Fig. 6, c).
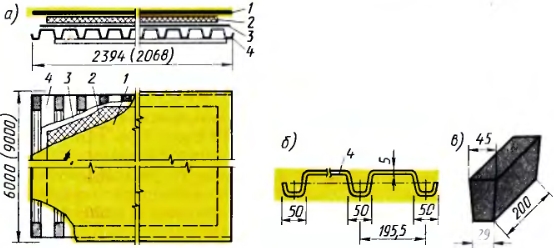
Fig. 6. The design of the coating panel of galvanized steel profiles:
a - cover panel, b - galvanized profiles, c - concrete liner in the corrugations along the edges of the steel roofing; 1 - roofing carpet, 2 - thermal insulation, 3 - vapor barrier, 4 - profiled flooring
Widespread panels of coatings based on metal sheet profiled increased factory readiness. In such panels, called metal two-layer panels (sometimes monopanels), polyurethane or phenolic foam is used as insulation, which is foamed between the metal sheet and the layer of waterproofing roll material in the factory.
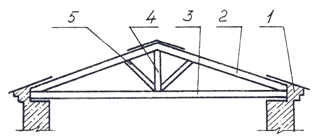
Rafters are divided into two types of construction: on-elephant, supported by the ends and the middle part (at one or several points) on the walls of the building, and hanging, supported only by the ends on the walls of the building (without intermediate supports).
According to the material distinguish wood and reinforced concrete rafters. Wooden rafters are used as supporting structures in the construction of temporary buildings, agricultural buildings, in the construction of wooden or brick buildings in rural areas. Reinforced concrete trusses are used in the construction of buildings with large spans (industrial buildings).
Suspended rafters (Fig. 7, a) are arranged when the distance between the supports (span) does not exceed 6.5 m. With one additional support, the width covered by the slant rafters can be increased to 10 ... 12 m, and with two supports - up to 15 m. The lower ends of truss legs 3 rest in wooden chopped or cobbled buildings on the upper crowns, in wooden frame buildings - on the upper trim, in stone ones - on the supporting beams 1 (mauerlates). The location of the rafters depends on the size of the contour of the building in the plan and the presence of internal supports in the form of walls or columns.
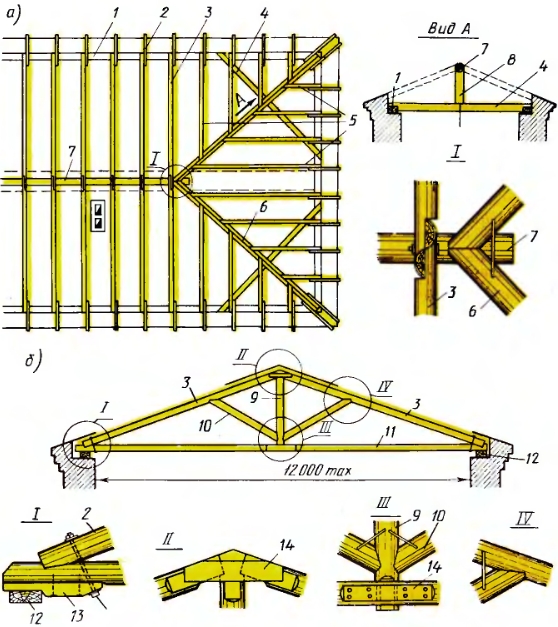
Fig. 7. Suspended (a) and hanging (b) wooden rafters:
1 - mauerlat, 2 - filly, 3 - rafter leg, 4 - beam for the support of the diagonal leg, 5 - ladies, 6 - diagonal leg, 7 - run, 8 - stand, 9 - grandmother, 10 - strut, 11 - tightening, 12 - supporting beam, 13 - podbalka, 14 - pad
Hanging rafters (Fig. 7, b) are two truss legs 3 connected by a tightening 11 at the bottom, which receives the thrust. To reduce the deflection of rafter legs with spans up to 8 m parallel to the tightening, a bolt is cut in (between the tie and top of the rafters), and with spans of more than 8 m, headstock 9 is installed. brackets, bolts and nails.
Farms are used in industrial construction with distances between walls and supports 12 ... 36 m.
The farm consists of a lower and an upper belt and a lattice between racks and braces enclosed between them.
Vapor barrier, made under the insulation on the supporting structure, protects the insulation from moisture penetrating water vapor from the room. The vapor barrier can be painting or coating in one or two layers, depending on the degree of humidity in the room.
As a paint vapor barrier using hot bitumen mastic or cold asphalt or bitumen-coker-solo mastic.
For okleechnoy vapor barrier used roll materials - roofing felt or glassine, pasted on hot bitumen, cold bitumen or bitumen-cookers mastic.
Thermal insulation is used to protect the building from cold and overheating by the sun. Thermal insulation can be monolithic, team and of bulk materials.
Monolithic insulation is made of lightweight concrete mixtures, such as perlite-concrete, lightweight aggregate, bitumen-perlite.
Prefabricated insulation made from slabs factory manufacturing. Such plates are produced from lightweight cellular concrete mixtures, foams based on polyurethane foam, polystyrene foam, hard mineral and semi-rigid slabs, perlitobeton, etc.
Thermal insulation of bulk materials is made of expanded clay, shungizite, perlite, vermiculite, etc. This thermal insulation is used in the absence of prefabricated insulation, as well as in integrated prefabricated panels.
44136
The choice of materials for the roof largely depends on the roof structure. Let's look at the main types of roofs and some of their individual elements. Roofs are divided into flat and pitched. Roofs of flat type are used for the construction of outbuildings (barns, baths and others). Residential homes are increasingly covered with sloping roofs. Pitched roofs can be divided into attic and bescherdachny. As a rule, attic roofs do not need thermal insulation. Roofs of bescherdny type can be warm (located above heated) or cold (above rooms that are not heated).
The attic can be used as an additional room for business purposes. It contributes to better ventilation of the house, if there is stove heating, then a chimney is located in the attic. Increasingly, in the attic, many craftsmen are arranging attic.
Types of pitched roofs
- lean-to, their support are two outer walls, which have different heights;
- dvukhskatnye, support for them are two outer walls, which have equal height;
half-hinged (or double-sloped), the upper parts of the end walls of which are cut off in the shape of a triangle (it is also called the hips);
hip, end slopes of such a roof have the form of beveled triangles, and the trapezoid side;
tent, four slopes of such roofs are made in the form of identical triangles, which converge at one point;
mansard or broken duplex roofs, each plane of them - these are two rectangles that are interconnected at an obtuse angle.
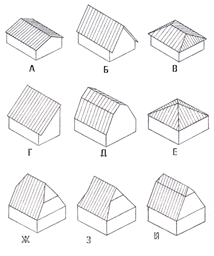 Types of pitched roofs
Types of pitched roofs
A - sloping duo-pitch;
B - steep dual slope;
B - hip gum;
G - odnoskatnaya;
D - broken (mansard) dvukhskatnaya;
E - tent four;
F, W, I - half-hip chetyrehpalm.
The most convenient and economical option are considered shed roofs, the slope of which does not exceed 5%. The internal space of the building is used to the maximum, while they can simultaneously be the ceiling in the economic buildings (bathhouses or sheds, garages, etc.), where strict horizontal position is not required.
If there is a need to use an attic for storing things, drying laundry or an attic device, then the roof of an apartment building is made broken or dvuhskatnoy.
Hip roofs are able to withstand wind loads better than others, but its construction is rather laborious, construction requires professional skills.
Making a choice in favor of a particular type of roof, do not forget to take into account not only operational, but also decorative characteristics. For example, a high roof on a one-story building will not only give it a more impressive and attractive look, but also allow the use of an additional attic room for its own purposes. In addition, on the steep slopes of the roof snow almost does not stay.
The main elements of the roof
The roof includes the following elements:
- supporting structure, which is created from the rafters, wooden beams or prefabricated trusses, which include the lower and upper belts and lattices of struts and bevels, located between them;
- the base under the roof;
- heat-insulating and waterproofing layer;
- proper roofing.
As for the roof beam construction, it is advisable to use it with a span length less than 4.5 m, and trusses - about 5-10 meters.

Rafters
Being an integral part of the roof, a very important function is assigned to the rafters: to support the crate. They take on the pressure of snow, moisture and wind, all roofing. By design, they are divided into padded and hanging. Suspended rafters are used if the span of the roof (the so-called distance between the supports) is less than 6.5 meters, and if there is an additional support - 10-12 meters.
Hanging rafters are used if the span of the roof does not have additional supports and is 7-12 meters. Their main difference from the naval ones is that they transmit only vertical pressure on the power plate. Tightening the lower waist and truss legs - these are the main components of the hanging rafters.
Suspended rafters:
- rafter foot;
- bolt;
- attic floor
Hanging rafters:
- mauerlat;
- rafter foot;
- tightening;
- grandmother;
- strut
Depending on the material from which the house is built, the rafter legs can be fixed:
- using the top strapping in;
- on the upper rims in chopped, wooden and block buildings;
- special support bars, which are also called mauerlat in stone buildings. In this case, the mauerlat should be 15–16 cm thick, it can itself be partial (the bars should be placed only under the rafter leg) or integral (run along the entire length of the structure).
If the rafter legs have a small cross section, then they can be prevented from sagging if you use lattices from struts, struts and a bolt. The struts and racks can be made of planks with a width of 15 cm and a thickness of 2.5 cm, or from wooden plates cut from a log with a diameter of at least 13-14 cm.
During installation, the rafter leg cuts in tightness. So that the end of the foot does not slide and does not flap the puff, you need to cut it in with a tooth, its height should be 1/3 of the puff height, with a spike, or taking into account both methods. In addition, the tightening will remain holistic and will not slip, if the rafters are installed at a distance of about 3-4 cm from the edge. The rafter leg needs to be cut into the end of the puff, and in turn, move the tooth as far as possible.

To strengthen the attachment of the rafter, you need a so-called double tooth. The teeth can be of the same height, but most often they are selected so that the height of the first is equal to 1/5 of the thickness of the puff, and the second - 1/3. In order to fix the first tooth, an emphasis is put on the thrust, a thorn and an eye on the rafter, and for the second - only an emphasis.
To further secure the rafters in the draws, you can use bolts or clamps. Bolts are not used as often as they can weaken the cross section of puffs and truss legs.
If the struts with a grandmother, they are connected with a cutting, while the nest is made in the grandmother, and a thorn is cut in the strut. The connection of this type in the hanging rafters needs additional fastenings with clamps or bolts. The crossbar connects to the rafter legs with a half-tree frying-stitch. Such a joint is fastened with a bolt and bolt, and in order to give it greater strength, it is also secured with a brace.
The main tightening elements are fastened together with a tooth, metal lining and bolts. Tightening connect with the grandmother with a clamp. To protect the walls of the building from atmospheric water, the roof overhang must have a length of at least 550 mm.
Besides the fact that the ends of the rafter legs are fixed in the inhaling, they are additionally hooked to the walls of the building with the help of the so-called twists. In this case, the roof will not be damaged in strong winds. Twisting is an impressive piece of thick wire, with one end it is attached to the rafter leg and the other to the crutch, it is driven into the seam of stone or brickwork at a distance of 30-35 cm from the upper edge of the wall, it is also possible to attic the ceiling of the attic. If the house is wooden, chopped, the twist can be replaced by an iron bracket that connects the rafters and the second crown of the log house.
Reinforced concrete trusses in nacelle rafters with one end must be laid on the outer wall of the building, and the second - on the precast girder of reinforced concrete, which is supported by brick columns. The lower ends of the truss legs, which protrude beyond the wall, are capable of carrying the eaves overhanging the roof. When you choose material for rafters, many factors need to be taken into account: the weight of the roof, the distance between the rafters, the length of the rafter and so on.
The base can be made from rolled or piece materials in the form of flooring or crates. For the manufacture of crates required the bars of wood, and for flooring - not only bars, but also boards. Solid flooring is advisable to do, if you choose to cover the roll material or asbestos cement tiles. For tiles, floorboards are laid out in one layer with a small gap, and for rolled material - in two layers: working and protective. For a protective layer choose narrow boards, which should be located at an angle of 45 degrees to the worker. Between the two decks you need to place the anti-wind ruberoid lining (ruberoid RPP-350 or RPP-300).
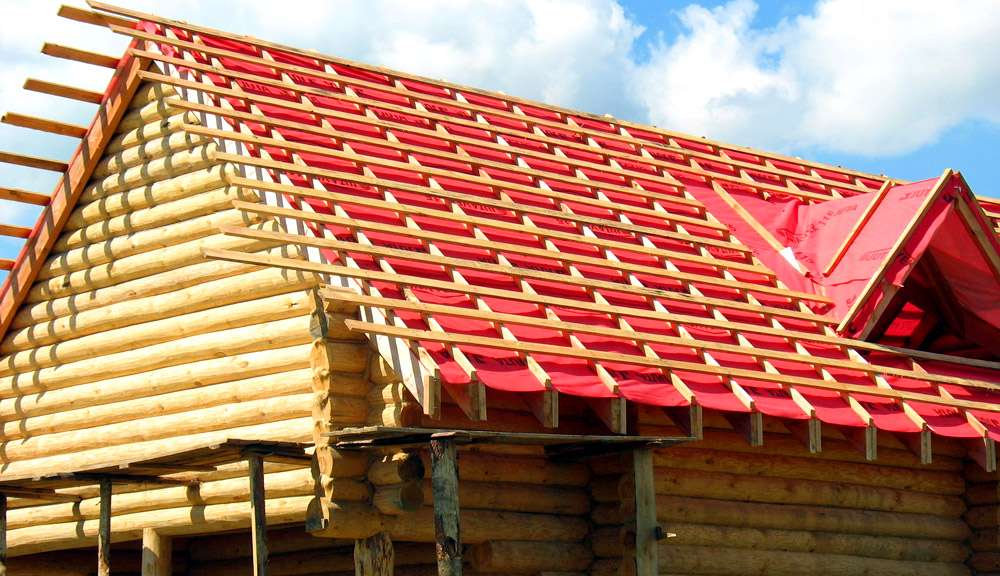

Lathing is required in cases where the roof will be covered with sheet steel, tile, wood or corrugated asbestos cement sheets VO (or slate).
Making the base, you need to follow two simple rules: each element must be securely attached to the supporting structures, and their joints should be in disperse above the rafters.
In addition, the specified distance between the bars or planks should be clearly observed over the entire surface of the base. The widest ones are located at the eaves, ridge or under the joints of the material for the roof, and the thickest ones (15-35 mm thicker than others) - near the eaves. Under the gutter the base should have a width of at least 750-800 mm, and under the overhang of the eaves with wall troughs the base should be equal to the width of the overhang. On the edges of the roof and in skates wooden bars should be installed on the edge.
Roof
Roofing is the top roof covering that provides protection against precipitation to all structural elements of the structure and drains water to the ground. That is why one of the main requirements that apply to the roof, is considered waterproof. The roof can be made of various building materials, asbestos-cement or steel sheets, roll and local (alumina and clay-alumina) materials.
As for the construction, the roofing can consist of:
- slopes (inclined surfaces);
- inclined ribs;
- ridge (horizontal ribs).

Endovy and gully - is the name of the intersection of the points at the incoming angle, and the cornice and gable overhangs are the edges of the roof that extend horizontally or inclined outside the building. Atmospheric water from the slopes of the roof is collected in the wall grooves, then it falls into the water receiving funnels, and then into the drainpipes and storm sewers.
Laying the components of the roof can be both in the transverse and in the longitudinal direction, connecting them overlap (most coatings) or in the lock (sheets of roofing steel).
According to the construction of the roof is divided into:
- single-layer (composed of sheets of VO, steel, asbestos cement tiles and folded tiles);
- multilayered (rolled materials, tes, shingle, shavings, flat shingles).
In multilayer roofs, the number of layers will vary from 2 to 5, it depends on the material you prefer. This roof is quite time-consuming and less economical. If in a multilayer roof each layer lies in the transverse direction, it must necessarily overlap the joints of the elements of the layer lying below. If it is placed in the longitudinal direction, it should cover the underlying layer with an overlap set by GOST.
The role of the roof slope is very large, because it helps to remove precipitation from the roof. It is expressed as a percentage or degree. Basically, when building houses, roofs are made flat, the slopes have the same slope.
From the slope of the roof, which you prefer, will depend on the material to cover, and the type of rainwater drainage from the roof. Drainage is organized (internal or external) and unorganized (external).
The structure of the internal organized drainage includes a standpipe, a water intake funnel, a discharge pipe and an outlet. This design can be used in all climatic areas.

The structure of the outdoor organized drainage includes gutters and external drain pipes. It can be used in climatic areas, where the water in the drainpipes almost does not freeze outside.
If the drain is unorganized, then water will drain along the entire length of the lower edge of the ramp; no additional devices are required. This type of drain is shown for climatic areas where rainfall is insignificant.
Roofing
All roofing work can be divided into 3 main groups:
- Procurement. This stage includes the selection, sorting or cleaning, cutting roll materials. Sheet steel made roofing elements, cut the slate, prepare mastic.
- Preparatory. The base under the roof is fully prepared.
- Major. Roofing materials are being laid, fixed to the base, taken care of after installation.
Endovy and drainage system
Enda, which form the incoming angle, are considered the most vulnerable elements on the roof, and precipitation accumulates in them at any time of the year. That is why it is necessary to approach the device of this element of a roof with all responsibility. Endova is a tray having a width of at least 300 mm, made of planks with a thickness of 25 mm. It is covered with galvanized, roofing or black painted steel, so that the ends of it go under the roof 200 mm from all sides.
The roof is the part of the building that encloses it on top of the external environment. The roofs of modern civil buildings are classified according to the following features:
Purpose;
Operating conditions;
Constructive features;
Roofing and carrier materials;
Thermal performance;
Types and sizes of products carrying part; degree of prefabrication and prefabrication.
The roofs perform the functions of supporting and enclosing structures of the upper floor of the building (the lower surface of the roof can serve as the ceiling of this floor) or attic. They are divided into two groups: bescherdnye combined, usually called coatings, and attic separate roofs. In addition, the roofs are ventilated and non-ventilated. Roofless roofs are divided into unexploited and exploited (flat).
According to the operational conditions, the roofs are arranged with external and internal drainage.
According to design features, roofs can be made of precast reinforced concrete panels (from heavy and light concrete), from complex insulated large panels (laminated), from wooden products. For coatings, attic panels are used as a carrier part. Combined insulated roofs (coatings) must meet heat engineering requirements. As a rule, roof panels overlap half the width of the building. The width of the panels is linked to the planning step of civilian buildings. Separate roofs are cold and insulated.
Rolled, non-roll and asbestos-cement materials are used for the roofs of modern civil buildings.
According to the degree of prefabrication, factory readiness of the roof, there are increased factory readiness (the roof or layers of insulation are applied at the plant) and lowered (layers of the roof are laid at the construction site).
Roofing in modern residential and public buildings provide for the use of roofs on unexploited separate and combined roofs with slopes of 1.5-5%. In separate solutions, depending on the operational requirements, flat roofs are adopted. The main types of roofing are: ruberoid or other roll; mastic as well as bezrulonnaya. Technical requirements for roofing are defined by SNiP 11-26-76.
For roofing use rolled materials and various mastics. Roofing material - roofing cardboard, impregnated with soft oil bitumen, covered on both sides with refractory bitumen
In the form of rolls also supply glassine and hydro-insol, stekloizol. Asphalt is used, as well as lining roofing material, for the lower layers of the roll roofing. Gidroizol made from asbestos paper or asbestos cellulose cardboard on bitumen. It is intended for flat roofs.
For mastic roofs, fiberglass made of alkali-free glass in the form of a grid (grade BB-G, BB-K) is used as a reinforcing gasket.
In addition to these main roll roofing materials of mass use, isolate, brizol, gudrokam, bitumen-polymer material, folgizol, polymer films are used.
Liquid quick-hardening materials are necessary for making rolled and mastic soft roofs - primers, pastes for sealing seams and mastic.
The main types of roofs with a minimum roof slope for civilian buildings in cities are shown in the table.
Unarmoured rolled and mastic roofs are covered with a protective layer. For unexploited roofs, such a layer is coarse sand or fine gravel (grains 5-10 mm), embedded in anti-septated mastic applied to roll materials. Concrete tiles and others serve as protection of the roll roof in the exploited coatings.
The base under the roofing carpet are reinforced concrete panels of the roof or screed, laid on a rigid roof insulation. In the cold period, instead of screed cement mortar arrange asphalt. Before laying the roof, carefully grout cement mortar joints between all prefabricated roofs, if necessary, overwrite their irregularities or minor defects, prepare vertical and inclined surfaces of the junction, to which the roof bends are glued, and also reinforce the slats, crutches and other parts necessary to fix the roof . The prepared base (panel and screed) is coated with a primer — a solution of bitumen in kerosene (1: 5 composition).
Fig. 1. Ruberoid and mastic roofing
Fig. 1a shows a four-layer ruberoid roof, in which each layer is shifted relative to the underlying by 250 mm (1/4 roll). The roof is laid on the mastic, starting from the eaves. In the northern regions of Russia, hot bituminous mastics of the MBK-G-55 grades for roofing carpet and MBK-G-85 are used for the stickers of the ruberoid roofing for abutments. In the areas of southern Russia, mastics are used, respectively, of the brands MBK-G-65 and MBK-G-100. The numbers in the marks mean the heat resistance of this mastic in ° C. In the cold, roll roofing should be performed on cold mastic. Mastered the production of rolled materials with a mastic layer applied on them, melted at a construction site before the roofing sticker has a special mechanism.
During the construction of the most significant objects, mastic roofs are used (Fig. 1, b). The masstry roofing is carried out in the following order: on the primer lining the rolls of fiberglass parallel to the ledge, mastic is applied to them, which impregnates the fiberglass and glues it to the roof base. Just put two more layers of fiberglass and mastic in mutually perpendicular directions. For this roof the use of a protective layer is mandatory. To perform mastic roofing, the use of two types of mastic is provided: hot bitumen and bitumen-rubber. Bitumen-rubber mastic has a brand of heat resistance, similar to hot bitumen, the conditions of their use are the same. The advantage of this mastic is that it can be cold (it can be used without heating).
When choosing the type of roof, it is necessary to take into account that, according to SNiP Sh-20-74, the construction of mastic roofs at negative air temperatures is not allowed.
Recently, a part of the layers of the roofing carpet is applied to large-sized roof panels in the factory, which significantly reduces the complexity of roofing in construction conditions.
The rules for the production of roofing works are set out in SNiP Ш-20-74. Their steady performance will provide the required quality of the roof.
Reliability of a roof with a small slope largely depends on the correct decision and high-quality execution of adjunctions to walls, pipes, drain funnels, eaves, etc.
In the examples shown in fig. 1, в, г, е, details of an adjoining of a roof to a parapet and walls are visible. So, the roof of roofing material (Fig. 1, c, e) comes to a vertical plane and ends on a side with a slope of 45 °. This side is made of cement mortar brand 50 or asphalt. In the place where the roof adjoins the parapet under the parapet slab (or a roofing steel cap), three additional layers of roofing material are added, which, together with the apron, are nailed with galvanized nails to the wooden rail. At the bottom of these three layers overlap one another at 100-150 mm. Similarly, it was decided to adjoin the mastic roof to the wall towering above the roof. Additional layers of mastic with fiberglass attached to the top of the rail. In both cases, the additional layers on top are covered with an apron made of galvanized roofing steel with a gap of 30 mm (Fig. 1, e).
In case of external drainage, special attention should be paid to the connection of the roofing carpet with the parts of the overhang and drainage system made of roofing steel (Fig. 1, e). A sheet of galvanized roofing steel, forming an overhang, is fixed with T-shaped crutches to the eaves slab. On this sheet, a high rebate is prepared, which, after the roll (or mastic) roof is laid, bend and clamp the edge of the roofing mat. Endovs located above the joints of the roof panels are covered with additional layers. The panels are covered with two additional strips of roofing material, of which the smaller one (200 mm wide) is laid dry, and the upper one (width not less than 330 mm) is glued with mastic along the longitudinal edges. On top of the endova, there are two additional layers of roofing material on mastic, the width of the top layer is 1000 mm (Fig. 2, a). A solution to the junction of the roll roof at the site of the expansion joint of the roof is shown in Fig. 2, e. This adjoining the roof is similar to adjoining it to a low parapet.
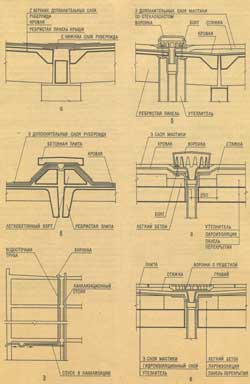
Fig. 2. Details of the roof and gutters
The use of wallless roofs has expanded in Russia and abroad. The device of such roofs has significant advantages compared with the roll. Due to the centralized preparation of the compositions and the mechanization of the process in the factory, the labor intensity and cost of work are significantly reduced. The quality and durability of roofs at the same time significantly increased.
According to SNiP 11-26-76, when using flute panels made of concrete with waterproof W-6 as a waterproofing roofing layer, it is necessary to paint the upper front surface of the roof panels with one of the recommended compositions: MBB-X 120 bituminous mastic with a 2 mm layer; Nairit solution with an NT grade of 1 mm; aqueous suspension of thiokol brand T-50 with a layer of 1 mm.
For bezrulonnyh roofs created polymer mastic roofing, which is based on a rubber-shaped polymer chlorsulfopolyethylene. Its physical and technical properties are high, it can be white and black. Roofing is applied to the roof panels as a paint at any temperature and vulcanized without heat treatment.
The possibility of using cationic bitumen emulsions consisting of 60-70% of a bitumen binder and an aqueous solution of a cationic emulsifier for wallless roofing has been experimentally tested. Emulsions are applied while reinforcing its layers with glass fiber, cut into pieces with a length of 20-30 mm.
The EGIK bitumen-polymer emulsion, applied on the concrete surface in two layers (roof thickness 6-8 mm), was developed and introduced.
Bituminous emulsion mastic, consists of bitumen, emulsifier (clay) and filler (fly ash, etc.). Such mastic is applied to the reinforced concrete roof products in the conditions of DSC installation with nozzles; a layer of mastic 4-5 mm. After drying, a light-protective composition with aluminum paint is applied over the mastic.
For roofs in use, the protective layer is made of concrete, cement slabs or asphalt concrete with a minimum thickness of 30 mm. These materials must have a frost resistance of at least F100. Plates should be laid on a layer of quartz sand 30 mm thick, poured onto the roofing carpet of five layers of hydro-insul or tar taro-felt on antiseptic mastic. When installing a funnel on the roof being used, coarse gravel and sand are used.
In the design and construction of civilian buildings with internal drainage from roofs, special attention should be paid to its rational solution. Water from internal drains should be directed to external networks of the combined or rain sewage system. Drainage of rainwater from internal drains into the domestic sewage system is not allowed. These conditions dramatically increase the cost of drains, so in practice they use a combined system of internal drainage, tested in Moscow in residential buildings of high number of storeys. They arrange the open drain of rainwater into the trays near the building, and in winter, the snowmelt water from the hydraulic drain gate is diverted into the domestic sewage system (Fig. 2, e), which is allowed by the norms.
As examples of installation of catchment funnels, three options were chosen: for a separate attic roof, for a flat, combined bescherdachnoy and for a flat operated roof (Fig. 2, b, d, f). The waterproofing roofing carpet adjoins the funnel. It is glued to the flange of the funnel or reinforced concrete panel. This junction is complemented by three mastic layers reinforced with fiberglass.
When installing the drain funnel on the panel of a separate cold attic roof, it is necessary to insulate the drain pipe within the attic with mineral felt or special heat-insulating shells