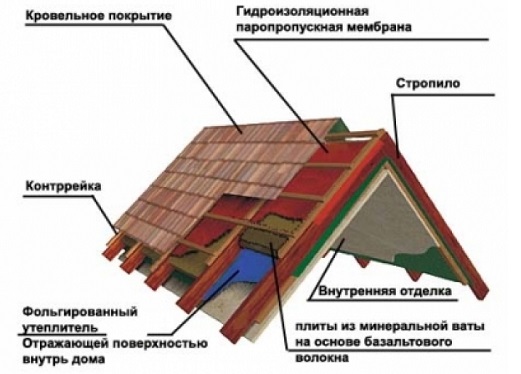
Types of coatings and requirements for them
Chapter 7. COATINGS
test questions
1. Basic requirements for floors, their classification and types.
2. Measures to improve the durability of wooden floors.
3. Constructive solutions for beam ceilings.
4. Features of the device floors of reinforced concrete flooring.
5. Basic design schemes of slabs of slabs.
6. Features of the device attic and over-basement ceilings.
7. Types of floors and their requirements.
8. Constructive solutions for floors of solid, piece and roll materials.
The structural element enclosing a building from above is called a covering. The main types of coatings are attic roofs, beschadacnye coatings, long-span flat and spatial coatings.
The main purpose of the coating is to protect the building from precipitation in the form of rain and snow, as well as from heat loss in winter and overheating in summer. It consists of supporting structures, perceiving the transmitted loads from the overlying elements, and the enclosing part.
Coatings have the following basic requirements. The design of the coating must ensure the perception of a constant load (from its own weight), as well as temporary loads (from snow, wind and the coating arising during operation). The enclosing part of the coatings (roofing), which serves to remove precipitation, must be waterproof, moisture-resistant, resistant to aggressive chemicals contained in atmospheric air and falling precipitations to the coating, solar radiation and frost, and not be subject to warping, cracking and melting. Coating structures should have a degree of durability consistent with the norms and class of the building.
To ensure the removal of precipitation cover suit with a slope. The gradient depends on the roofing material and the climatic conditions of the construction area. Thus, in areas with heavy snowfall, the slope value is determined by the conditions of snowfall and snow removal; in areas with heavy rains, the slope of the roof should provide quick water drainage; in the southern regions, the slope of the coating, as well as the choice of roofing material, is determined taking into account solar radiation.
Roofs are usually made in the form of inclined planes-slopes, covered with a roof of waterproof materials.
In the attic roofs, a room (attic) formed between the carrier and the enclosing part of the covering is used to house the engineering equipment (central heating pipes, ventilation ducts and shafts, machine room, lift compartment). To enter the attic make stairs, doors or access hatches. The height of the attic for movement on it people take at least 190 cm. For lighting and ventilation of the attic in the roof arrange attic windows (Fig. 7.1, d).
The shape of sloping roofs depends on the shape of the building and architectural considerations (Figure 7.1). Roof slope expressed in degrees of inclination of the slope to the conditional horizontal plane (Fig.7.1, e) through the tangent of this angle in the form of a fraction or percent.
In buildings of small width often lean-to-roofs (Fig. 7.1, but). The roof of a building with a drain on two opposite sides is called a gable. The edge of the dihedral angle formed at the top of the roof by two slopes is called with skate(Figure 7.1, b).
The intersection of the slopes forming a protruding oblique angle is called nakosnym edge, and the falling corner is end or bastardThe lower part of the ramp is called down and the lower edge of the slope is roof edge. The end of the dual sloped roof can be solved in the form pediment(Figure 7.1, d). A pediment is formed if the slopes of the roof overlap the end wall of the house and protrude in front of it.
Fig.7.1 - The main types of forms of attic pitched roofs:
but - leaning; b - dvukhskatnaya; at- Roof with attic; g - tent, d, e - general view and plan of the roof of the house; well- an example of building a roof slope; and, to - half-gable ends of a gable roof; l, m, n, o - deployment schemes of attics and air gaps of the roof; p - scheme of formation of ice on the cornice; r - a dormer window; with- designation of roof slopes; 1 - overhang of the roof; 2 - dormer window; 3 - tympanum pediment; 4 - gable; 5 - horse; 6 - ramp; 7 - gable; 8 - Endova; 9 - nakosny edge; 10 - hip; 11 - pivotum; 12 - air inlet; 13 - exhaust opening; 14 - snow and frost on the eaves; 15 - grille shutters
The roof of a square or multi-faceted building has triangular slopes - hips (Figure 7.1, g). If the inclined ramp cuts off not the entire end of the gable roof, but only the upper or lower part of it, then the incomplete end ramp is called a half-grip (Fig. 7.1, and).
The line of intersection of two slopes of the roof, forming a prominent dihedral angle, is called nakosnym edge (Figure 7.1, to). The line of intersection of the roof slopes (the line of valleys and cut edges) runs along the bisectors of the angles between the walls (Fig. 7.1, e, well), therefore, when constructing a roof plan, it is necessary to follow this rule, if the house has right angles, then the projections of the cut edges are drawn in a plan at an angle of 45 °.
Inside the attic, it is advisable to arrange residential attic space (Figure 7.1, at), which in stone buildings are separated from the attic by firewalls, and in wooden buildings - by non-combustible partitions.
For ventilation, use is made of dormer windows and windows arranged in gables and semi-gables of semi-hinged roofs, filled with shutters of the “blind” type, which allow air to pass through well and prevent rainwater from entering the attic. Dormer windows are placed at a height of 1-1.2 m from the level of the attic floor.
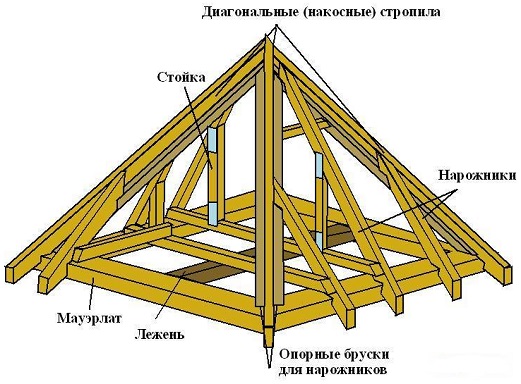
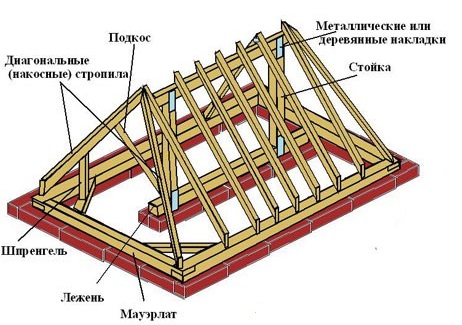
Bearing structures of pitched roofs consist of rafters and battens. Rafters - the main supporting structure of the roof, which, based on the walls or individual supports of the building, determines the number of slopes and the angle of their inclination. Rafters are made of wood in the form of logs, boards or boards. All matings of individual elements of the rafters are made with the help of cuts and metal fasteners (brackets, bolts, nails, clamps). Rafters are oblique and trailing. Oblique called rafters, the main elements of which - rafter legs - work as inclined laid beams. The length of such beams should be no more than 6.5 m (maximum length of standard commercial wood). Hanging rafters (Fig.7.2) represent the simplest type of truss trusses, where inclined truss legs convey thrust for tightening (lower truss belt).
The simplest type of inclined rafters is used for single-sided roofs (Fig.7.3). Rafter legs are based on parallel bars - mauerlat, laid on the upper edge of the walls. Mauerlat are used to evenly distribute the load from the rafters to the wall. They are isolated from the stone wall with a gasket.
In the presence of supports inside the building, gable ramps are also used. In this case, the deck is laid on the inner supports (with the inner wall) or runs (with free-standing supports), on which racks are installed every 3-4 m as supports for the upper, ridge run (Fig.7.3). Rafter legs are supported on the upper girder and power plates. To give rigidity in the longitudinal direction from the racks to the upper girder down the struts, which, reducing the span of the upper girder, makes it possible to reduce its cross section.
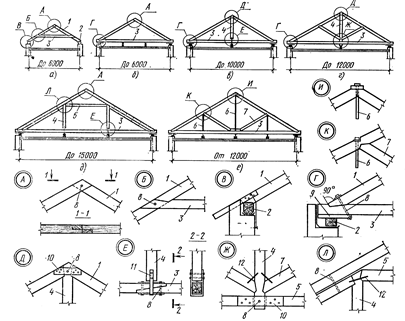
Fig.7.2 - Hanging rafters (trusses):
but - with a raised pull; b - with the tie used for hanging the attic floor; at - with hanging grandma; g- with the suspended grandma and struts; d - with two suspended attendants; e- metal-wooden farm; 1 - rafter foot; 2 - mauerlat;
3 - tightening; 4 - suspended grandma; 5 - strut; 6 - steel rack farm; 7 - strut; 8 - bolt; 9 - shorty; 10 - wooden lining; 11 - clamp; 12 - bracket
With an asymmetrical arrangement of internal supports, the upper girder does not coincide with the ridge of the roof. In this case, the horizontal design is introduced into the overall design. scramble, which gives additional rigidity in the transverse direction and dampens the thrust that occurs in the design. The fight is made of planks and placed below the upper girder. When spanning a truss foot more than 4.8 m, a strut is brought under it, which makes it possible to reduce the cross section of the truss leg and, like a scrum, gives additional rigidity in the transverse direction.
To prevent demolition of the roof in a strong wind, the rafter legs (usually one) are attached with wire twists to the crutches (or ruffs) being hammered into the wall.
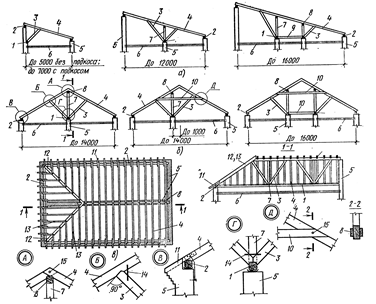
Fig.7.3 - Inclined rafters:
but - leaning roofs; b - the same, gable; at - plan rafters; 1 - lying down; 2 - Mauerlat; 3 - strut; 4 - rafter foot; 5 - wall; 6 - attic floor; 7 - stand; 8 - run; 9 - strut; 10 - scramble; one 1 - filly; 12 - nakosny (diagonal) rafter foot; 13 - a lawyer; 14 – bracket; 15 – bolt
The hip chute is formed by means of diagonal (slanting) truss legs and women squad - shortened truss legs based on the mauerlat and diagonal truss foot. The step of rafter legs choose from calculation of optimum flight for boards or bars. Usually it is taken equal to 0.7 m for a batten batten and 1.2-1.5 m for a bar stone.
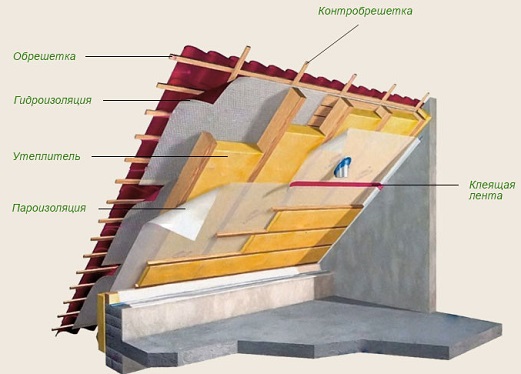
Crate is the immediate basis for the roof and is arranged on the rafter legs in the form of flooring of boards or boards. The nature of the flooring, whether solid or discharged, depends on the roofing material used.
The top waterproofing layer of the roof, which is supported by supporting truss structures and crate, is called a roof. For pitched roofs use different roofing materials, each of which requires a certain slope of the slope. The roof is made of sheet steel, asbestos cement sheets, tiles or rolled materials (Fig. 7.4).
Fig.7.4 - Roofs of pitched roofs:
but - from roofing steel; b, at - from flat asbestos cement tile; g - roll; d - tiled; e- from wavy asbestos cement sheets; 1 - Mauerlat; 2 - drainpipe; 3 - gutter; 4 - crutches; 5 - hook; 6 - wall gutters; 7 - standing seam; 8 - a lying fold; 9 - crate; 10 - truss legs; 11 - double fold; 12 - single standing seam; 13 - asbestos cement sheets; 14 - fastener; 15 - Ruberoid; 16 - asphalt; 17 - tiles; 18 - asbestos cement sheets
The leader of roofing materials in the world for several centuries is ceramic tile. Its advantages include fire resistance, durability, environmental friendliness. The disadvantage is the large weight and complexity of installation.
Traditionally, tiles used in the western and south-western regions of Ukraine. It is produced in small volumes and is currently being squeezed out of the construction by metal tiles.
The metal tile is made on the basis of a metal sheet, profiled under the tile pattern, with a multi-layer protective coating and with a color range of over 30 tones.
The service life of the roof of metal is 50 years. It withstands any climatic conditions and air pollution by industrial emissions.
Shingles - the perfect roofing material that adorns the house, cottage or cottage. It fits perfectly into the modern urban landscape and is relevant against the backdrop of the rural landscape.
The advantage of a soft tile is simplicity of installation on roofs with various a slope and a configuration.
The multi-layered shingles provide absolute waterproofing, which eliminates corrosion and rotting of the base. The top layer of slate dressing of various colors protects shingles from climatic influences and provides a long period of operation (up to 15 years).
Profiled flooring slabs produce both trapezoidal and undulating profile, they are used for wall cladding, as well as roofing.
Slate roofs continue to lead in mass construction due to the low price and ease of installation.
For the device vapor-permeable waterproofing layers in the under-roof space are intended under-roof diffusion films. Their application is necessary first of all when using a metal tile, and also other roofing materials.
The use of diffusion films provides:
a) protection of attic from dust penetration;
b) protection of garret rooms from residual rain and melt water;
c) conditions for air circulation necessary for ventilation of the roofing space and, as a result, for ensuring effective roof insulation;
d) removal of water vapor from the insulation (due to microperforation).
To increase the fire resistance of wooden structures of roofs, they are painted with lime or special solutions. All wooden structures that work in contact with the stone should be carefully antiseptic and only roofing or roofing felt should be laid between them.
Bare-handed (combined) coatings perform with a slope of up to 5%. They can be ventilated (Fig.7.5, at) external air through air gaps or channels in the top of the panel in order to avoid condensate and non-ventilated (Fig.7.5, but, b) from solid or multi-layered panels.
Water from the combined roofs is diverted by internal drainage (organized drain). From the attic, water can be drained through gutters, drainage funnels and drainpipes (organized drain) and unorganized drainage system, which directly discharges water from the roof edge. In case of unorganized water drainage, an overhang of the eaves of at least 550 mm should be provided.
- a necessary element of the building structure. These covers can be attic and bescherdnymi, odnoskatnymi, gable and chetyrehskatnymi, poluvalmovym or poluchiptsovym. Regardless of the choice of the roof structure of the house, this element should effectively fulfill its main functions: to protect the building from wind, sun, rain and snow, to serve as a reliable heat insulator.
Roofs and roofs: structural elements (with photo)
The roof structure has a bearing and enclosing parts. The bearing part of the roof structure consists of wooden or reinforced concrete rafters, wooden, steel construction trusses or reinforced concrete panels. The device of the roof supporting structure transmits the load of snow, wind and its own weight to the walls and individual supports. The enclosing part of the roof structure consists of the following elements: the roof - the upper waterproof roof sheath, and the base under the roof in the form of a batten of wooden bars, plank flooring or cement layer on a reinforced concrete base.
Look at the photo of the roofs of the house, how the supporting and enclosing structures look:
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Roofs, depending on the material, are made of wood, of earthen, roofing sheet steel. Roof roofs made of corrugated asbestos cement sheets (slate), flat asbestos cement tiles, rolled materials - tol and roofing material are rarely used nowadays.


The supporting structure of a sloping roof should have the necessary strength and stability, the enclosing part should be lightweight, resistant to chemical and weathering, waterproof, low thermal conductivity.


By design types of roofs can be bescherdnymi and garret. For ventilation and attic lighting in the roof arrange attic windows.


When constructing a roofless roof, the elements of the attic floor and the roof are combined in one design - the floor protecting the building from cooling in winter and precipitation.
These photos show the roof structures of various types of houses:
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
What degree of slope should the roof have?
To ensure the flow of atmospheric water, the surface of different materials must have a corresponding slope, which is expressed as the ratio of the lifting height h to half of the span spanning L or in degrees of the angle of inclination of the roof to the horizon L. For example, at L = 27 the ratio H: L = 1: 2. When sloping roofs, the slope is sometimes expressed as a percentage, for this ratio H: L is multiplied by 100.
Depending on the slope of the roof are flat and pitched. Flat roofs have a gradient of no more than 3%. Pitched roofs are systems of intersecting inclined planes - slopes. The intersections of the roof slopes form two-sided corners, of which the upwards are called ribs, and the ones facing downward are blunt-edged or endov. The upper horizontal edge of the intersection of the roof slopes is called the ridge.
The slope of pitched roofs is accepted depending on the type of roof, for example, for clay tiles the slope of the roof is 1: 1-1: 2, for roofing sheet steel 1: 3.5 (L = 16).
Depending on the slope of the roof, they are called flat or steep. Sloped roofs with a slope of up to 15% are flat, with a slope of more than 15% - steep.
 What slope should the roof have ideally? When choosing the shape of the roof, special attention should be paid to the possibility of rapid and complete draining of rain and melt water. To reduce snow loads (in the Moscow region, the regulatory snow load is more than 100 kg / m2), roofs with steep slopes with a slope of more than 30 ° should be designed. As practice has shown, the greatest amount of snow accumulates on the leeward slopes of roofs with a slope of 30 °, since from the windward slope the snow is blown away by the wind, transferred through the ridge and deposited on the leeward slope. However, familiarization with the projects of cottage houses shows that in many cases, the roofs, unfortunately, have a slope of exactly 30 ° (perhaps it is easier to draw on a square). On roofs whose slopes are significantly more or less than 30 °, the amount of snow will be less, since with a steep slope, for example 45 °, the snow easily slides off the roof, and with a small slope it is blown away by the wind. It should also be borne in mind that if tall trees grow close to the cottage, protecting it from the wind, then significant snow deposits will form on the roof.
What slope should the roof have ideally? When choosing the shape of the roof, special attention should be paid to the possibility of rapid and complete draining of rain and melt water. To reduce snow loads (in the Moscow region, the regulatory snow load is more than 100 kg / m2), roofs with steep slopes with a slope of more than 30 ° should be designed. As practice has shown, the greatest amount of snow accumulates on the leeward slopes of roofs with a slope of 30 °, since from the windward slope the snow is blown away by the wind, transferred through the ridge and deposited on the leeward slope. However, familiarization with the projects of cottage houses shows that in many cases, the roofs, unfortunately, have a slope of exactly 30 ° (perhaps it is easier to draw on a square). On roofs whose slopes are significantly more or less than 30 °, the amount of snow will be less, since with a steep slope, for example 45 °, the snow easily slides off the roof, and with a small slope it is blown away by the wind. It should also be borne in mind that if tall trees grow close to the cottage, protecting it from the wind, then significant snow deposits will form on the roof.
Roof form: single, gable and four slope structures
In the construction, various forms of roof are used, which are selected taking into account the general configuration of the building in terms of plan, the possible direction of water diversion, as well as individual architectural possibilities.


Shed roof constructions are rarely used nowadays, they are arranged over buildings of relatively small width and in cases where water can only be discharged to one of the longitudinal walls.


Constructions of gable (gable) roofs consist of two slopes, directed in opposite directions. The resulting triangles in the upper part of the end walls are called tongs or gables.


The hip hipped roof construction has ramps on four sides. Ramps directed to the end walls are called hip, hence the name of the roof - hip. Gable walls in the design of hipped roofs are missing.


A variant of the hip roof is a semi-hip or semi-gable roof. Side ramps cut only part of the gable and therefore have a length along the slope line that is less than the main ramps. Half hip located at the top, has the shape of a triangle.
The choice of material and type of roof construction depends on the location of the internal supports in the building, the size of the spans to be covered, the roof slope and roof requirements: fire resistance, thermal performance and durability.
Bearing structures of pitched roofs
The simplest type of supporting structure of pitched roofs are sloped wooden rafters. The sloping rafters of the gable roof rest on the lower ends on the subrafter bars — Mauerlat, and the upper ones — on the horizontal bar, called the upper ridge girder. The upper girder is supported by racks mounted on internal supports. The distance between the racks, carrying ridge runs, take from 3 to 5 m.
To increase the longitudinal rigidity of the construction of the rafters and reduce the cross section of the ridge girders, paired longitudinal struts located at each rack or through one with small spans are reinforced. To reduce the free span of the truss legs, install transverse struts supported on the bottom of the bed and supporting the truss legs at the top. In case of displacement of the inner support from the central axis of the building by no more than 1 m, the rack supporting the girder is set obliquely.
With two longitudinal capital walls in a building or two rows of internal columns, two upper girders are laid. Legs and in this case, the length can be integral. To increase the rigidity of the structure it is necessary to install bolts.
The design of the truss system hip roof hipped roof
In the hip roofs of hip roofs, at the intersection of the slopes, it is necessary to place diagonal stitched trusses, cut shorter truss feet into some - crooks.


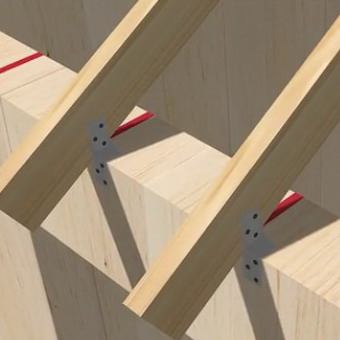
Diagonal truss legs in the truss construction of the hip roof are long and carry a significant load. Therefore, they are supported in flight by an intermediate support in the form of a strut or a trussed structure placed in the corner of a building. With the construction of the truss system of the gambular roof, the lower end of the diagonal truss foot is supported on the subrafter bars in the corner, at the place of their interfacing or on the beam, laid obliquely on the subrafter bars at some distance from the corner. If there is one pass, the upper end of the diagonal leg rests on its console, and when there are two runs, it rests on holes that are attached with nails to the ends of the rafter feet. Run consoles are used as intermediate supports on slanting legs. In places of conjugation, rafters are reinforced with metal fasteners: nails, bolts, clips.


In buildings that do not have internal supports, it is impossible to arrange inclined rafters. Therefore, construction trusses are used as supporting roof structures, to which the attic flooring is suspended.
Located along the upper contour of the truss, the rods form the upper belt of the construction truss, along the lower contour - the lower belt. Racks - vertical rods and braces - inclined rods located between the upper and lower belts form a truss grid. Roof trusses produce wood, steel and reinforced concrete. In the longitudinal direction of the farm is set at a distance of 4-6 m from each other. The simplest type of wooden construction farm are trussed trusses. The trusses consist of truss legs, a puff, a perceiving thrust, a vertical suspension - the headstock to which the puff is hung, and struts.


Due to the large width of the building when installing trussed and building trusses, it is unacceptable to overlap the attic floor with beams that rest on the walls. The construction of the attic floor is suspended on steel clamps for tightening the rafters or to the lower truss belt, forming suspended floors.
In the presence of a suspended attic ceiling suspension or headstock hanging trusses, working in tension, sometimes made of steel cords. By tightening wooden hanging rafters suspended in the direction perpendicular to it on the clamps made of steel strip wooden girders. Perpendicular to the girders, wooden beams are suspended, between which lightweight inter-girder filling is laid. To reduce the load when mounting a roof structure on hanging rafters or a truss truss, you should choose a construction for a suspended ceiling that has a low dead weight.


In steel farms, suspended attic floors are made non-combustible on steel beams. Precast reinforced concrete slabs are placed between the beams, light insulation and armored concrete or armorosilicate slabs are used for them. When insulating the attic attic, it is necessary to protect the steel beams from cooling, since condensation of water vapor will cause the lower flange of the beams to rust, and unwanted yellow stripes may form. In order to increase the fire resistance and durability, the supporting structures of pitched roofs should be made of reinforced concrete, and the reinforced concrete supporting structures of pitched roofs are recommended to be made without use of large-sized prefabricated panels.
Roof Anti-icing Cable System
 The cable system against icing of the roofs consists in the fact that along the perimeter of the roof they pull an electric cable that operates when the temperature of the air is from 0 ° C to -15? C and if there is water or ice on the roof. The system is equipped with temperature and humidity sensors that are installed on the edge of the roof on the south side. Using sensors regulate the on and off cable system.
The cable system against icing of the roofs consists in the fact that along the perimeter of the roof they pull an electric cable that operates when the temperature of the air is from 0 ° C to -15? C and if there is water or ice on the roof. The system is equipped with temperature and humidity sensors that are installed on the edge of the roof on the south side. Using sensors regulate the on and off cable system.
More expensive control systems make it possible not only to turn the heating on and off, but also to set the operating time depending on the temperature: the roof gets warmer the longer, the stronger the frost.
Before installing the system, pay attention to the quality of the cable. The cable must have a strong internal braid and a reliable insulation layer made of resistant material to ensure the mechanical strength of the cable and the electrical safety of the system.
Butt of the gable roof and the height of the attic floor
In most projects, the shape of the roof of the cottage - gable. The end of the house roof can end with a vertical brick wall of a triangular shape with a cornice at the upper edge and a belt at the bottom, that is, it can be solved in the form of a pediment. Of course, not classical, such as above the columns of the Bolshoi Theater in Moscow or the Parthenon temple in Athens, but very expressive, with good proportions, perhaps with a window and decorative details. Such an end of the gable roof allows for good natural lighting and ventilation in rooms located in the attic, and also makes the structure of the rafters uniform, although a slight increase in the volume of brickwork is obtained.


Another option for the formation of a roof at the end wall is a hip solution, that is, with inclined triangular slopes. Such a roof does not increase the volume of the attic brickwork, but it also complicates the construction of the rafters. Sometimes, for example, according to the plan of the architect, the end slope cuts not the entire end of the gable roof, but only the upper or lower part of it. In this case, the incomplete end slope is called a half-hilt, and the roof is called a half-hinged. For the formation of hips wide houses establish diagonal rafter legs, and on them - shortened rafters (narozhniki). Elements in wooden trusses are mated with staples, nails or bolts.


The height of the attic roof is determined by the width of the house, the slope, the roof structure and the need to ensure a free fire passage with a height of at least 1.6 m along the whole room. It is important to ensure that in the lowest places, at the outer walls, there should be at least 0.4 m from the top of the attic floor covering to the power plate. This is a necessary requirement for the periodic inspection and repair of the lower parts of the rafters, which are most exposed to blowing, freezing, moistening, as well as to ensure fire safety. Note that high roofs not only delay snow less, but also allow for more efficient use of attic space.
Installing rafter roof rafters (with video)
The bearing part of the roof is most often formed by a system of inclined wooden trusses. Their common name is truss legs. They are installed at an angle equal to the angle of inclination of the roof slope, and their lower ends rest on external brick or block walls through a lining in the form of a longitudinal beam (mauerlat) attached to the wall for uniform load distribution.


When installing rafter girder roof between the wall and the mauerlat laid two layers of roofing material. The upper ends of the rafters are supported on a podonkovy bar or on intermediate girders that transfer the load on the internal load-bearing walls through a system of racks. The overall stability of the truss system is provided by braces, struts and diagonal bracing.
![]()

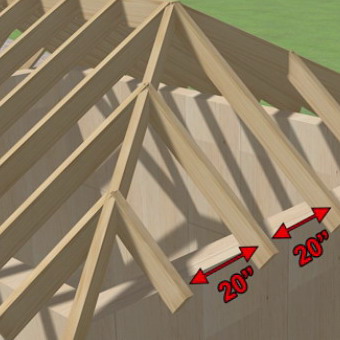
Rafter legs are located every 0.8-2.0 m depending on their cross-section, roofing material and other conditions. The lower ends of the truss legs through one should be attached to the wall with wire twists to protect the roof from possible breakdown in a strong wind. Twisting is fixed for a crutch or ruff, hammered into the seam of masonry 250-300 mm below the power plate.

![]()
In houses with timbered or cobbled walls, the rafters are connected by brackets to the second upper crown. For the purpose of accessibility of the power plates and the lower ends of the truss legs for inspection and repair, they are placed 35–40 cm from the floor.


In cases where, when installing rafters on the roof, they rely only on two external walls (if there are no intermediate supports), they are called trailing and represent the simplest type of truss trusses, to which they hang (if they have one) attic floor. In hanging rafters with the spans of more than 6 m between the upper ends of the rafter legs clamp pendant (vertical bar). In order to avoid sagging of the structure, horizontal tightening and girder for supporting the attic floor beams are suspended to the lower end of the headstock using strip steel clamps. For spans up to 12 m, struts are introduced into the structure of the rafters, reducing the estimated length of the rafter legs.
After what period do racks for girders and rafters are installed?
Racks under the girders are installed on the internal walls every 3-4 m, while under the rack lay boards (lezhny) and gaskets of roofing material or roofing felts.


Criteria for the complexity of the truss system are associated with design constraints or additional requirements for certain types of roofing of the roof. For example, 1 m2 of ordinary tile weighs about 50 kg, so when using this material the rafter system should be designed for maximum load. Lumber consumption, and hence the cost of the roof in this case will increase by 15-20%. Soft tiles are lighter than ceramic by a factor of five, but it requires a continuous crate of planks or plywood, the use of lining carpets for small slopes, and this makes the savings imaginary.
Watch the video “Installing roof rafters” to better present the process technology:
When constructing overhangs of roofs and eaves, in order to save a large-sized timber, the lower end of the rafter leg is increased by short boards - filly (40 x 120, 50 x 100 mm), which are also easier to pass through the brickwork.
The design of the roof of the cottage: the most common questions
Choosing the shape and construction of the roof, inexperienced builders have a number of questions: the most common and the answers to them are given below.
What types of specialists do roof structures have?
Constructions enclosing buildings from above are mainly of two types: pitched or garret; flat or besherdachnye, in which the roof and the attic floor combined (the so-called combined coverage). The latter consist of a supporting structure (for example, beams or reinforced concrete slabs that simultaneously perform the function of a ceiling. For removing precipitated precipitates, roofs are always made with a slope. Depending on the design needs, the coating also includes a vapor barrier and heat-shielding layer. Flat, non-scratch coatings are widely used in residential construction multi-storey and public buildings in industrial and agricultural buildings.In cottage-type houses in domestic practice, they are extremely seldom. There are bescherdnye roofs and curvilinear, arched forms, for example, in swimming pools, gyms and exhibition halls.
What design roof cottage is preferable?
For cottage type homes, as a rule, they use attic or pitched roofs. They consist of the upper part (shell), called the roof, the base (lathing or solid flooring), which directly supports the roof, and the supporting structure - rafters, supported on external and internal walls. Roofs more than other elements of the house, are exposed to weathering. The cost of their maintenance and repair significantly affect the cost of operating the whole house. Therefore, roof structures must have strength and durability that corresponds to the class of the building. The roof reveals the silhouette of a cottage house, as if crowning it, gives a finished look and expressiveness to its architectural solution. She, like an elegant hat, completes and often defines the image of a fashionably dressed person.
Do not complicate if unnecessary constructive beauty functions that should perform the roof?
In developing the project of the cottage, the shape of the roof should be given considerable attention, including its visual appeal. At the same time, one should not allow excessively complex outlines, which, without adding beauty to the house, complicate the constructive decision, make construction, operation and repair more expensive. In addition, it can lead to the formation of large snow bags on the roofs and, as a result, leaks. Roof slopes are in degrees relative to a horizontal surface, for example, 45 °, or percent.
What loads must the roof withstand in central Russia?
Standard load ranges from 70 to 200 kg / m2 horizontal projection of the coating. In addition to the constant load from its own weight, the roof structure must withstand temporary loads (snow cover, wind pressure on the windward side and vacuum pressure on the leeward side), as well as loads arising during operation (repair, cleaning from snow and others).
What deformations occur in the roof bearing structures?
Deformations and other deficiencies in roofing supporting structures are encountered during operation. In wooden: violations of the joints between the elements, destruction of the waterproofing with a mauerlat, rotting and bending of the rafter legs, crates and other elements; in reinforced concrete: destruction of a protective layer of concrete, corrosion of reinforcement, deflection, cracks, etc .; in sheet steel roofs: weakening of the ridges and folds, corrosion, holes and fistulas, destruction of the paint or protective layer; in the roofs of asbestos cement tiles and other piece materials: damage and displacement of individual structures, insufficient overlap on each other and weakening of the fastening of the elements of roofs to the batten. All of them are eliminated as they are identified, preventing their further development.
The roof is not only protection from various atmospheric phenomena, but also the aesthetic beauty of the whole building. The unique design and structure will give individuality to any home.
Today there are a huge number of various types of roofs. All of them are used in construction, both private houses and multi-storey buildings. Regardless of the type, all the roofs consist of two main parts. The supporting structure is represented in the form of rafters and crates and the roof itself.
The shape of the roof is chosen depending on various factors. These include: the size of the building and the purpose of the building.
Roof types
Now the most common are the following types of roofs:
- single slope;
- gable;
- chetyrehskatnaya;
- flat;
- hip.
All other varieties are derived from these types.
Shed roof
Shed roof is the easiest option roofing. The name speaks for itself. This roof has only one ramp. Such structures are mainly used for small private houses, cottages, as well as in the construction of the garage. Such roofs have several advantages. The first distinct advantage is the ease of installation. Indeed, the construction of a shed roof does not require the involvement of many people and special equipment. The second advantage is the use of a minimum amount of building material. That is why the shed roofs are widely used in the construction of garages and country houses.
The angle of inclination of a single shed roof is often less than 25 degrees, so the wind does not greatly affect the integrity of the structure.
There are, of course, disadvantages that should be considered when using a shed roof. The main disadvantage is the absence of an attic. Another disadvantage is the inconspicuousness of a shed roof. It does not look as impressive as, say, a gable or chetyrehskatnaya.
Gable roof
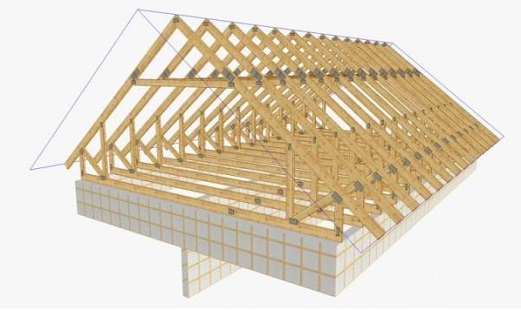
The gable roof is a roof that has two ramp sloped to the outer walls. This type of roof is considered optimal for the construction of small houses. In this embodiment, the rafters abut each other. They make up pairs that are tied together by a crate. At the ends, this roof has triangular walls. Under the roof is set loft. This advantage allows gable roofs to remain the most popular option in modern construction. In addition, the appearance of a gable roof is much more attractive than that of a single slope.
If we talk about the installation process, it is quite simple. All rafters are installed in pairs parallel to each other. They communicate with each other by crates. The lathing is made of the simplest bars. Then various insulating materials are laid, and only after that the roof itself is mounted.
Quadrant roof

The four-slope roof is one of the most common options today. It has an attractive look and high durability. The four-pitch roof can be either hip or hip. Tent option consists of four triangles that converge into one, forming a peak.
This option is used in cases where the building box is a square. If the box of the building is rectangular, then in this case a hipped four-slope roof is installed. it consists of two triangles and two trapeziums. Of course, this design is more complicated, but it looks more attractive than the roof tent version.
The height of such a roof may be different. It is pre-calculated before installation. The four-pitched roofs are now very popular, however there are certain drawbacks to them. The most important is the complexity of the design. Such roofs, especially the hip version, require the attraction of additional labor, and the construction is sufficiently complex.
Therefore, if we are talking about a simple small building or a summer house, then it is worth trying to install another simpler option in order not to get a pretty penny.
Hipped roof
Hip roof is now widespread throughout construction. She has an attractive design as well as beauty. Many install a similar roof on their private houses or cottages.
Hip roof forms a pyramid. At its base should always be square. Its constructive elements are four triangles whose vertices converge at one point.
This type of roof saves on construction material, as it does not provide for the installation of gables. Naturally, the base must necessarily have a square, otherwise the construction will not turn out to be complete. It is necessary to strive for a square base, but you can do something similar to this geometric shape. Most importantly, all the vertices of the triangles meet at one point.
There is one very significant drawback with hipped roofs - this is the complexity of the roof system.
Flat roof
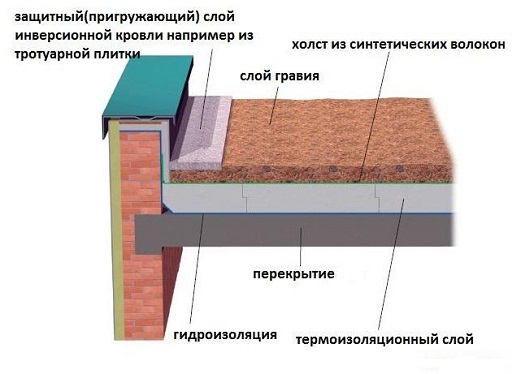
Flat roofs are used in the construction of high-rise public and residential buildings. Such roofs are very often called bescherdnymi. It is considered that such roofs are more economical than pitched ones.
For the installation of a flat roof, it is necessary to expend significantly less material than for the installation of a sloping roof of any option. The surface area is significantly less than the coverage area of the pitched options. That is why flat roofs are used in high-rise construction. The material that is put on such a roof can be any, even the cheapest. Common slate is most commonly used. Such roofs are not visible from the ground. The beauty of such structures is in second place. On the first - construction savings.
There are several types of flat roofs: traditional, inversion, operated, green and so on. All these types are widely used in high-rise construction.
Roof structure
Any roof consists of three components: the carrier, thermal insulation and the roof itself.
Let us consider in more detail each component.
The most commonly used tree in the form of rafters. They can be sloped or hanging. Suspended rafters lean ends and the middle part of the walls of the building. The hanging ends rest on the walls of the building without the use of intermediate supports.
All rafters are mounted vertically. In this case, the minimum distance between them must be at least one meter. All rafters communicate with each other by crates.
Elements of truss construction are made of bars.
Thermal insulation layer of the roof
If we are talking about non-residential attic room, the attic flooring is subjected to insulation. In the case when it comes to the attic, it requires insulation of all surfaces.
For insulation used a variety of materials. You can use the usual mineral wool, but it will have to lay additional layers of vapor barrier and waterproofing. Thermal insulation is needed for any residential building. If we are talking about a summer cottage, you can do without it.
Roofing roof
The roof is the topmost layer of the roof. Roof coverings currently exist a huge amount. The most widespread slate and metal. Their main goal is to protect the building from the harmful effects of the external environment.
Roof angle
The angle of the roof depends on many different factors. The main ones are: the material from which the roof is made, the type of roof, the climatic features of the region in which the construction is made.
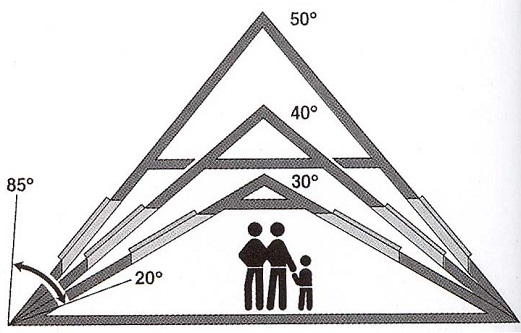
All these factors are necessarily taken into account when calculating the angle of inclination. With a large amount of precipitation, the angle increases, and with strong winds decreases. The most effective angles are from 10 to 60 degrees.
The height of the ridge of the roof and raising the rafters are determined with the help of a square. You can also calculate these values. To do this, the span width is divided in half, and then multiplied by a certain coefficient from the table.
Roof rafter system
Rafters and roof trusses are of two main types - naslonny and hanging. The main truss at the moment - a triangle. It is the most rigid and economical. If we talk about roof trusses, then they consist of complex roof beams, racks, struts, and so on.

Suspended rafters. Such structures are installed in houses with an average load-bearing wall. Consist of two inclined truss legs. Their lower ends rest on the longitudinal bars, and the upper ones on the ridge girder.
Hanging rafters. They are used where there are no internal supports. They rely solely on exterior walls. They consist of sloping truss legs and a horizontal bar for the perception of thrust from truss legs.
How to build a roof properly do it yourself
Consider the option of installing a pitched roof with your own hands, as the most common today. Consists of the following sequence of actions:
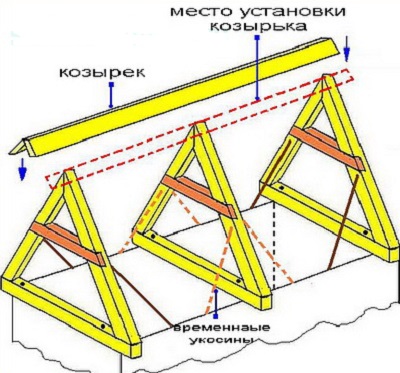
- installation of rafters;
- installation of ridge beam;
- the device crates;
- roofing.
Consider the process of installing the roof do it yourself. Sometimes the rafters are lowered over the edge of the wall. This is done to ensure that moisture that drains from the roof does not fall on the walls of the house.
The rafters themselves gather on the roof. Moreover, all elements must be prepared in advance. Upstairs only assembly. The result is a truss farm, which consists of two truss legs, puffs and racks. After assembly, the structure is raised vertically to the very place where it should be installed. Next, it is attached to the power plate. As additional temporary fixings boards are used.
After that, all trusses are connected by a ridge bar. After that, you can begin mounting crates. The material can be used unedged board with a thickness of 25 millimeters. It significantly reduce the cost of the roof. Each board is nailed to the rafters with nails, the length of which is 70 millimeters.
The design of the batten depends largely on what material will be laid on the roof. If you plan to use metal tile, then unedged board will not be suitable for creating crates. In this case, it is better to take the timber.
Once the crate is installed, you can proceed to the installation of roofing. It is very important to check the flatness of the battens and trusses before starting work.
Roof mounting

Installation of the roof is quite complicated. In most cases, you will have to seek outside help. Alone, the roof is quite difficult to mount.
Installation of the roof consists of several stages. It will be a question of a house where people live all year round, that is, it is necessary to install not only the crate, but also thermal insulation.
The entire installation process will include the following steps:
- installation of truss system;
- installation of the batten;
- laying insulation;
- installation of roofing material.
As you can see, the work is quite voluminous, but interesting. Its implementation must be approached very carefully.
So, it all starts with the installation of a truss system. It is set in place. Pre-prepared bars for rafters on the ground.
Once the rafters are installed, you can proceed to the installation of crates. It can be made from both boards and bars. It largely depends on the type of building and the type of roofing material.
Thermal insulation is necessary in those houses where year-round living is planned. In addition to the thermal insulation material, it will be necessary to install waterproofing and vapor barrier to protect the house from external weather factors.
The last stage is the installation of roofing. Currently, the most popular is metal. It is worth remembering that if you use this material, you will have to make the crate of wooden bars, as the boards do not fit.
The roof initially performs the function of a shell covering the building, designed to protect it from external, atmospheric influences. Rain, snow, melt water, thunderstorms, wind - all these elements are opposed by a light, at first glance, construction, but in reality a reliable, carefully thought out roof that can withstand the strongest onslaught of natural forces. The main advantages of any roof - light, durable, economical roofing material, simplicity and ergonomic design.
- roofing;
- crate frame;
- tyvek Solid (Soft) membrane for warm waterproofing;
- heat insulating material;
- mineral or glass wool with a thickness of up to 100 mm;
- h96 Silver film or H110 Standard film as a vapor fill for a warm roof;
- thick polyethylene, or Tyvek Solid waterproofing membrane, or D96 Silver film (D110 Standard) for cold roofing;
- qSB plates or lining with a waterproof impregnation for the inner skin of the cake (for the attic) with a thickness of 9-12 mm;
- construction knife for cutting hydro and thermal insulation; - building stapler, staples; - tape connecting SP1.
For arranging a cold attic, waterproofing is attached to the crate (with sagging up to 20 mm), and glass wool is rolled directly onto the attic floor. Steam-filler is attached to the ceiling from the living space.
Roof–The upper structure of the building which serves to protect against atmospheric influences (rain, snow), fluctuations in the temperature of the outside air, sunlight and wind. The roof consists of supporting and protecting elements. The top waterproof layer enclosing the roof sheath or cover is called the roof.
Roof - the top element of the roof (coating), which protects buildings from all types of weathering.
The shape and construction of the roof are divided into: pitched and flat. Pitched are:
Shed roof- its plane (slope) rests on the bearing walls having different heights. This roof is most suitable for the construction of outbuildings.
Gable roof consists of two plane-slopes, based on the supporting walls of the same height. The space between the slopes, which has a triangular shape, is called pliers or gables. A kind of gable roof is the attic.
Hip the roof consists of four triangular slopes, converging at one upper point. The roof formed by two trapezoidal slopes and two end triangular is called hip cheek (There are and gable hip (half-hardened) when gables are cut off
Flat roof - consists of plates resting on bearing walls having the same height.
Types of roofing materials:
Asbestos cement flat sheets, tiles, corrugated asbestos cement sheets, clay tiles, coating of smooth metal sheets (steel, aluminum, copper), two-layer roll materials (bituminous, bitumen-polymer and polymeric materials)
Structural elements of the roof:
The main components of the roof supporting structure are the truss truss and the sheathing.
Crate - batten boards are the basis on which the roofing material will lie
According to the method of attachment to the walls of the house, there are two types of supporting structures - it is hanging and naked.
Impulsiveit is used for the roof of relatively small buildings, with the size of the size of the span (the distance between the supporting structures) :
up to 6 m - without installation of internal supports (racks)
up to 14 m - with the installation of one rack on the supporting structures (and the rack is not necessarily installed exactly in the center of the truss system - it can be shifted asymmetrically to one of the walls)
up to 16 m - with the installation of two supports
This type of rafters is called “inclined” because they are superimposed on the top of the mauerlat, and also if there is a ridge girder, a longitudinal element connecting the tops of all the roof trusses.
Hanging rafter design. It is so named because the ends of the rafters rest only on the external load-bearing walls, without intermediate supports inside the building.
Since, under the weight of the roof, rafters on the walls of the building create stubborn loads on the walls of the building, the rafters provide a pull that compensates for the force that is generated.
Definitions:Mauerlat- piping along the top of the supporting walls, to which the lower edges of the rafter legs are attached. Transmits load from rafters to external load-bearing walls.
Rafter legs used to secure and hold the roofing material
Seahorse - the ridge is the place where two or more roof slopes meet.
Fillyis a piece of board by which the rafters are extended for the device of the eaves overhang
QUESTION 13. Ladders. Requirements for the stairs. Classification of stairs by purpose, materials, design schemes
Ladders are used to provide communication between rooms located on different levels (floors), as well as for emergency evacuation of buildings.
Also, all ladders must meet certain regulatory requirements, among which the most significant are the following:
- the width of the staircase for the main stairs should not be less than 0.8 ... 1.0 meters;
- stairs should be well lit, especially the first and last steps;
- all ladders with more than three steps must be equipped with strong and reliable railings, the height of which must be at least 90 cm;
- the height of the step (riser) should not be more than 20 cm, and the width of the step (tread) should not be less than 25 ... 30 cm;
The main types of stairs consist of marches and platforms.
March- this is the sloping part of the ladder along which the ascent or descent to certain levels of a building or structure is carried out. Dividing constructive elements between marches are staircases, which are located horizontally at the beginning or end of the march. The staircases located in the floor level are called floor, and those located between floors are intermediate or interfloor.
The assembled flight of stairs consists of steps and inclined beams supporting them. Beams that support steps only from below are called kosourami, and supporting steps simultaneously from the bottom and from the ends - bowstrings.
In general, the stairs can be classified as follows:
- by functionality - brownies, landscape and special;
- to destination - interfloor, entrance, workers, checkpoints;
- by design - with risers, without risers, with bowstrings or on kosoura, screw (with or without a central stand), with cantilever, suspended, retractable, stop steps, etc .;
- on the material of supporting structures - wooden, steel, stone, reinforced concrete, concrete, combined;
The steps are subdivided into privates and friezes adjacent to the landing.
The horizontal plane of the steps is called tread, and the vertical is the riser. The height of the steps (h) is 135-200 mm, width (b) not less than 250 mm.
Standard stair slopes: 1: 2; 1: 1.5; 1: 1.75 and 1: 1.25. The main stairs have a slope of 1: 2 with steps of 150x300 mm.
The number of steps (rises) in one march between platforms should be from 3 to 16 pieces, and in single-marches - up to 18 pieces. "
In order to determine the dimensions of the stairs and the staircase, it is necessary to know the height of the floor, choose the scheme of the stairs (double-march or three-march), its slope and size of steps.
QUESTION 14. Partitions. Purpose and types. Partitioning requirements. Classification by materials and structures. Fastening to walls and floors.
Bulkheads - it is not bearing vertical fencing separating adjacent buildings of the building.
Support for partitions are load-bearing elements of the ceiling, and for the first floors of baseless buildings - brick columns or concrete preparations. It is not allowed to rest partitions on floor structures.
Partitions are classified by:
1. Location: interior; interroom; for kitchens and bathrooms. Interroom apartments should have increased sound insulation, and for kitchens and bathrooms - moisture resistance.
2. According to the method of the device: from small-sized and large-sized elements; of small, arranged directly on the site of brick, small blocks; large-sized prefabricated prefabricated.
3. By material: from brick, wooden, gypsum boards, cellular concrete, gypsum board, glass-reinforced stone, glass blocks.
Brick partitions are made with a thickness of 1/4 brick (brick on the edge) with vertical and horizontal reinforcement with 4–6 mm wire or half-brick thickness with their reinforcement with pack steel of 1.5x25 mm, laid in horizontal joints of the laying every six rows. Masonry brick partitions of 1/2 brick is not reinforced, if their length is not more than 5 m, and the height is less than 3 m.
Partitions of glass profile glass. They are moisture resistant, have a good appearance and, most importantly, a large light transmission capacity. Partitions and glass blocks are laid out on a cement mortar with a gasket in the grooves between the blocks of steel vertical and horizontal reinforcing bars. They are assembled from elements of different profiles, having a height equal to the height of the room, set between the upper and lower straps and the seams between the profiles are sealed with special mastic.
The board partitions are made of boards 50 mm thick, mounted on the bottom trim, and the upper ends are fixed with triangular bars attached to the ceiling. Then the partitions are plastered on both sides by dribble with a lime-plaster solution with a thickness of 20 mm or sheathed with plasterboard sheets. Shield partitions have a greater degree of industrialization. The shield is made of two three-layer silt on the entire height of the room with quarters to ensure their docking with each other. If it is designed for plastering wet, then they are covered with tears. Frame partitions consist of a wooden frame and filling. The frame is a series of racks installed in 0.5 ... 1 m, which are sheathed on both sides with boards with a thickness of 20 ... 25 mm. The gap between the boards filled with loose aggregate (slag, expanded clay, etc.) then plaster or upholstered with plasterboard sheets. Partitions of gypsum and gypsum concrete slabs with a size of 800 x 400 x 80 m are installed on a gypsum solution. For better bonding and protection from cracks in the seams of the slab, they are manufactured with grooves located in the lower and side faces. Formed between the plates, the installation channel is filled with plaster mortar. Single-layer partitions with a height of up to 4.5 m erected without a frame, but in places of doorways and reinforced through wooden racks. In order for partitions and gypsum boards not to crack, they must be installed on solid bases that are not subject to deflection or draft.
According to the method of construction partitions are prefabricatedmounted from large-sized elements; performed on-site from piece materials (slabs, bricks, stones, lumber) or monolithic reinforced concrete.
In accordance with the purpose of the partition must have a small mass and thickness, and must also have certain sound insulation qualities, fire resistance and durability. To partitions bathrooms and kitchens make high demands on the hygienic surface finish, in addition, partitions bathrooms should be moisture resistant.